Energy In The Form Of Light
Energy In The Form Of Light - However, bulbs and torches also emit it. Artistic rendition of a photon (not physically accurate). However, neither a classical wave model nor a classical particle model correctly describes light; Let us understand it in detail. Light energy is a form of electromagnetic radiation of a wavelength, which can be seen by the human eye. Web we would like to show you a description here but the site won’t allow us. Web watch newsmax live for the latest news and analysis on today's top stories, right here on facebook. A single photon, which is the smallest bit of light possible, carries the following properties: Here light is assumed to travel as wave packets of energy hv, and if v (frequency) exceeds threshold fr. The consequence of molecules’ absorbing light is the creation of transient excited states whose chemical and physical properties differ greatly from the original molecules.
Gamma rays are the highest. Web saying that light is pure energy would imply that light only carries the property of energy and no other properties, which is simply not true. Researchers have now coaxed two ions into forming a phonon laser containing fewer than 10 phonons, placing it firmly in the quantum regime [], whereas previous phonon lasers had at least 10,000. Light is made of tiny photons which contain lots of energy. Light energy is always moving and can therefore not be stored. Artistic rendition of a photon (not physically accurate). Web light energy each orbital has a specific energy associated with it. Chemical energy is energy stored in the bonds of atoms and molecules. Sun is the primary source of visible light. These types of energy include infrared (ir) rays (heat waves given off by thermal bodies), microwaves, and radio waves.
A type of electromagnetic radiation invisible to the human eye. Light energy is a kind of kinetic energy with the ability to make types of light visible to human eyes. Web this is the result of electronic processes within the molecule of the dye or pigment by which even ultraviolet light can be transformed to visible—e.g., blue—light. The other types of em radiation that make up the. Radio waves are the lowest energy. These types of energy include infrared (ir) rays (heat waves given off by thermal bodies), microwaves, and radio waves. Space is dark because light is only visible when it has an object of which to bounce off. Web light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Light has a dual nature that is revealed only in. However, neither a classical wave model nor a classical particle model correctly describes light;
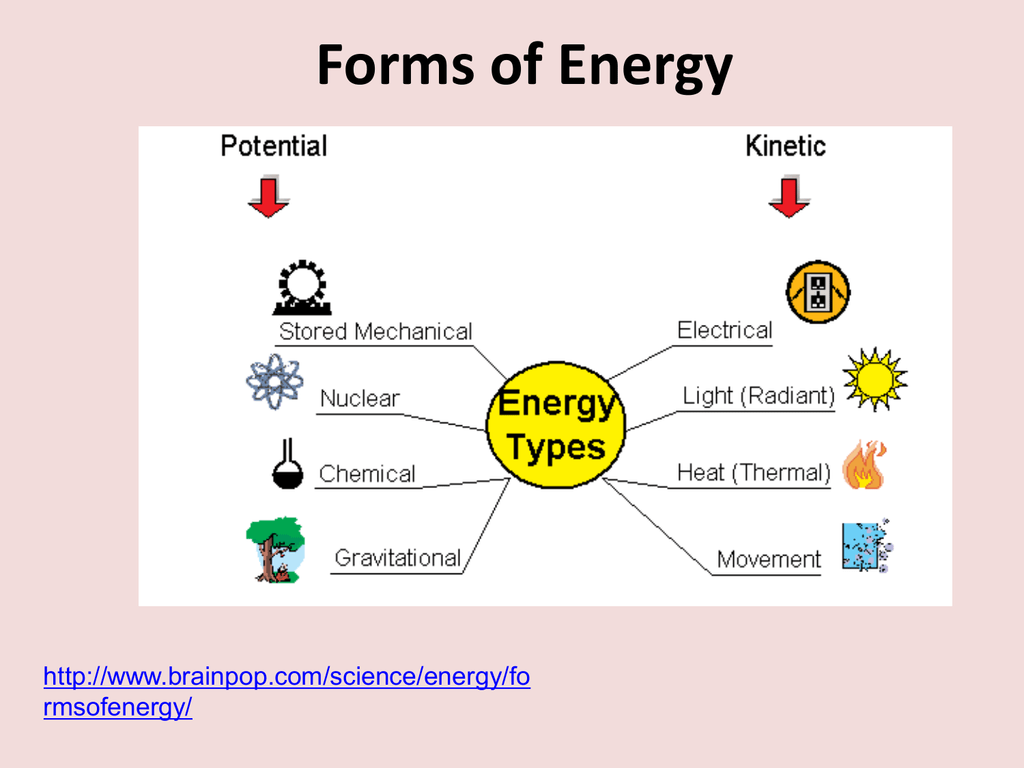
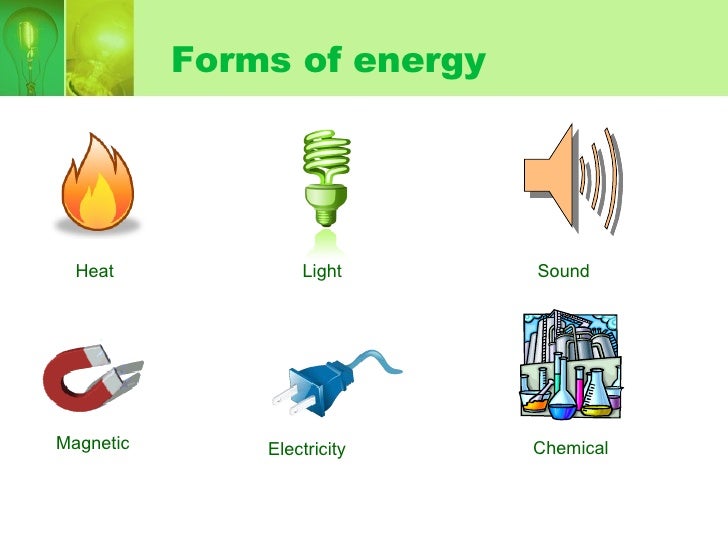
Forms of Energy
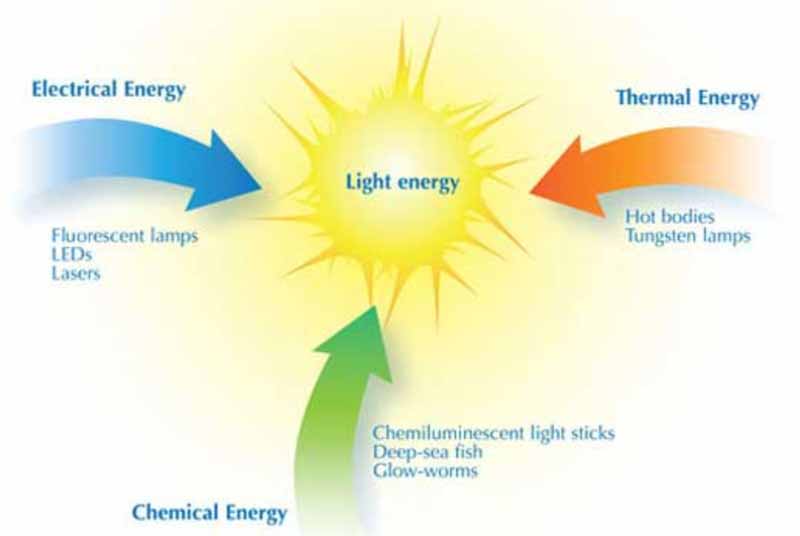
A solar panel converts light energy to electrical energy by a process called photoelectric effect. Any form of light has electromagnetic energy, including parts of the spectrum we can't see. Forms of energy basics +menu forms of energy many forms of energy exist, but they all fall into two categories: Potential energy kinetic energy potential energy potential energy is stored.
Concept 25 of Example Of Light Energy To Chemical Energy
Light is known as a type of electromagnetic radiation produced by hot objects such as lasers, bulbs and sunlight. View solution > a beam of light consists of a bundle of light rays. The intensity of photons is dependent upon the amount of energy they contain. The speed at which light travels in a vacuum. The name incorporates a latin.
Sources of light energy
Web light is a form of energy that causes a sensation of smell. However, bulbs and torches also emit it. The other types of em radiation that make up the. Web light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Department of health & human services 330 c street, s.w., washington, d.c.
Understanding light and other forms of energy on the move Science
The intensity of photons is dependent upon the amount of energy they contain. Web all forms of light travel at the same speed (the speed of light), but they carry different amounts of energy. Light energy is a kind of kinetic energy with the ability to make types of light visible to human eyes. Web phonon lasers replace the light.
PPT Light Reflection and Refraction PowerPoint Presentation, free
Web saying that light is pure energy would imply that light only carries the property of energy and no other properties, which is simply not true. These types of energy include infrared (ir) rays (heat waves given off by thermal bodies), microwaves, and radio waves. Your eyes are detectors of visible light energy. Light energy is always moving and can.
Light Energy Forms of Energy
Light is defined as a form of electromagnetic radiation emitted by hot objects like lasers, bulbs, and the sun. The consequence of molecules’ absorbing light is the creation of transient excited states whose chemical and physical properties differ greatly from the original molecules. Potential energy kinetic energy potential energy potential energy is stored energy and the energy of position. Department.
Gazpacho is not tomato soup Unit 5 Heat and light.
Light energy is a form of electromagnetic radiation of a wavelength, which can be seen by the human eye. Sun is the primary source of visible light. However, neither a classical wave model nor a classical particle model correctly describes light; Web light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Radio waves are.
Light Energy Knowledge Bank Solar Schools
Light has a dual nature that is revealed only in. Any form of light has electromagnetic energy, including parts of the spectrum we can't see. Light is known as a type of electromagnetic radiation produced by hot objects such as lasers, bulbs and sunlight. It is a type of kinetic energy. The other types of em radiation that make up.
Forms of Energy Thermal energy, Chemical
Web to the right of the visible spectrum, we find the types of energy that are lower in frequency (and thus longer in wavelength) than visible light. These types of energy include infrared (ir) rays (heat waves given off by thermal bodies), microwaves, and radio waves. However, bulbs and torches also emit it. Web light or visible light is electromagnetic.
Simply Skilled in Second Forms of Energy & a FREEBIE!!!
Light energy is a kind of kinetic energy capable of allowing various forms of lights visible to the human eyes. Light energy is always moving and can therefore not be stored. Web what is light energy? Web watch newsmax live for the latest news and analysis on today's top stories, right here on facebook. A type of electromagnetic radiation invisible.
A Single Photon, Which Is The Smallest Bit Of Light Possible, Carries The Following Properties:
Visible light energy, such as from a light bulb, fireflies, computer screens or stars, is one form of electromagnetic energy. Low income home energy assistance program (liheap) liheap does not charge a fee for receiving a benefit. Web phonon lasers replace the light excitations (photons) that are used in a standard laser with vibrational excitations of matter (phonons). A solar panel converts light energy to electrical energy by a process called photoelectric effect.
Light Is Made Of Tiny Photons Which Contain Lots Of Energy.
Web what is light energy? View solution > light is a form of _____ that we can detect with our _____. Light has a dual nature that is revealed only in. Your eyes are detectors of visible light energy.
Web Electromagnetic Energy (Or Radiant Energy) Is Energy From Light Or Electromagnetic Waves.
Light energy travels in the form of waves. Light energy is a kind of kinetic energy capable of allowing various forms of lights visible to the human eyes. Space is dark because light is only visible when it has an object of which to bounce off. Web what is light energy?
Web Light Is A Form Of Energy That Causes A Sensation Of Smell.
Light is defined as a form of electromagnetic radiation emitted by hot objects like lasers, bulbs, and the sun. Radio waves are the lowest energy. The name incorporates a latin term and means “below red.” infrared light has wavelengths longer than those visible to humans. The speed at which light travels in a vacuum.