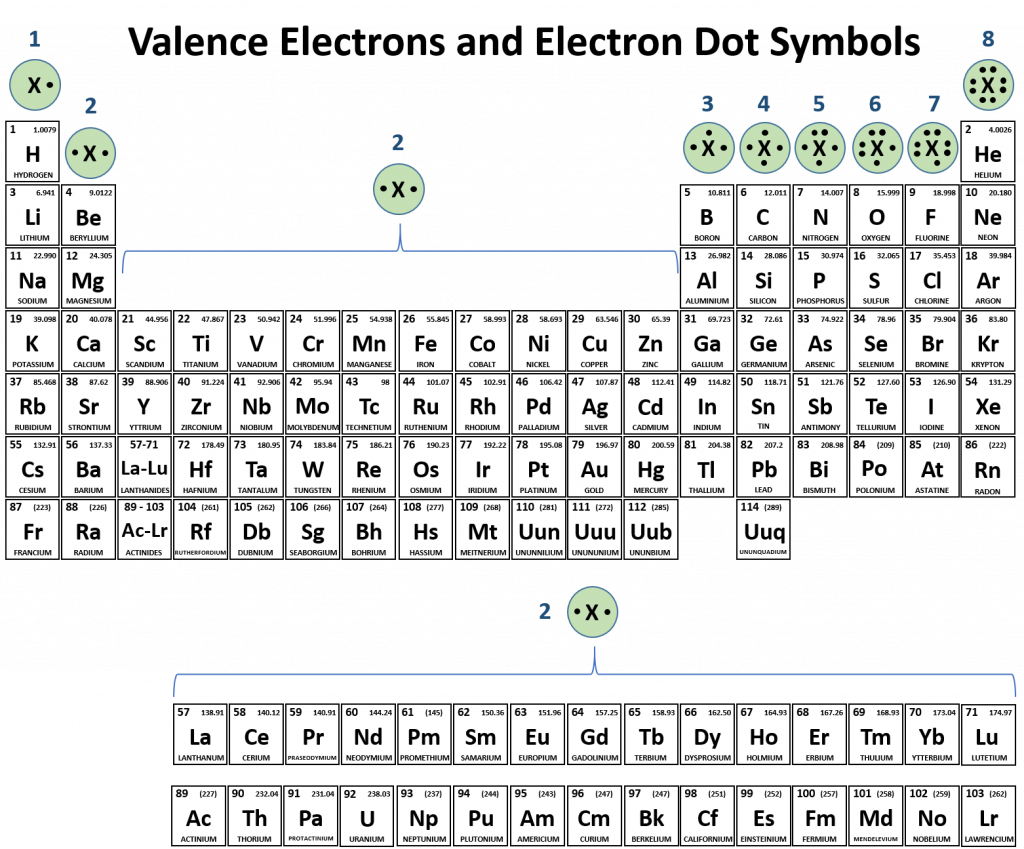
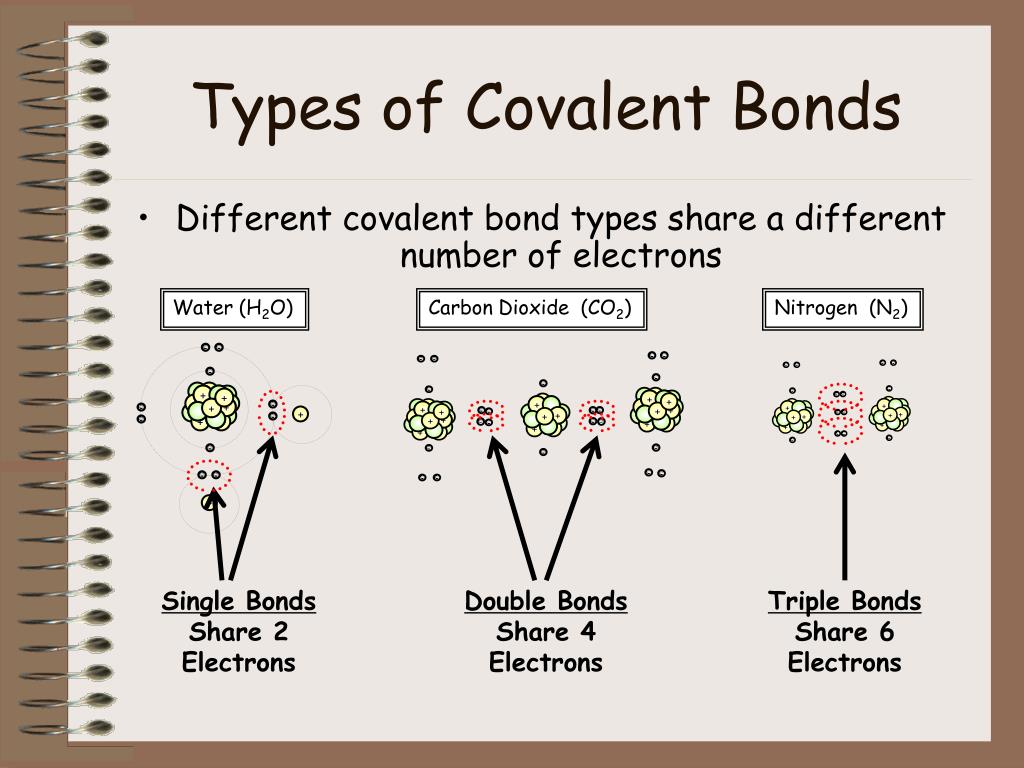
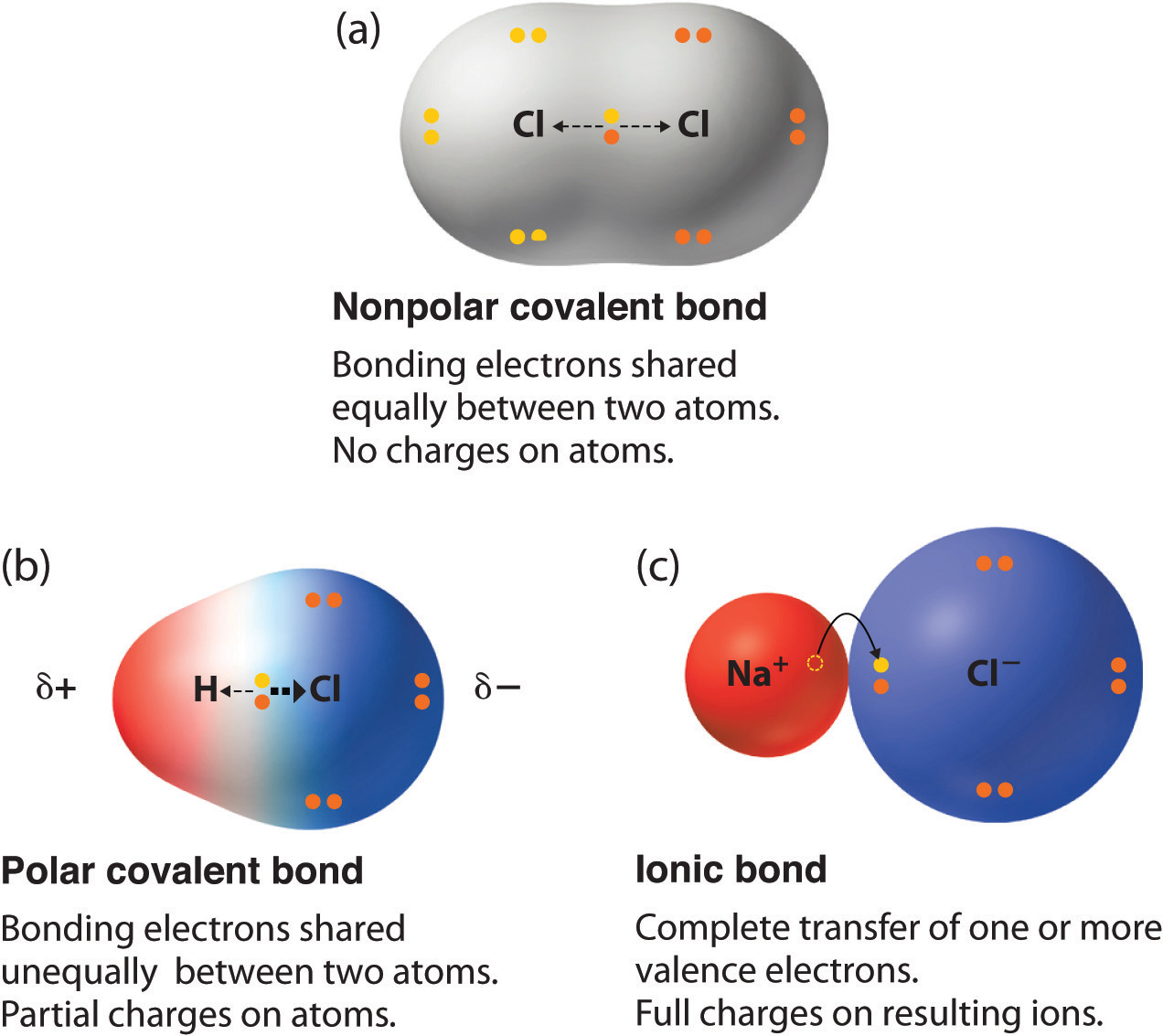
Which Two Atoms Would Typically Form A Covalent Bond
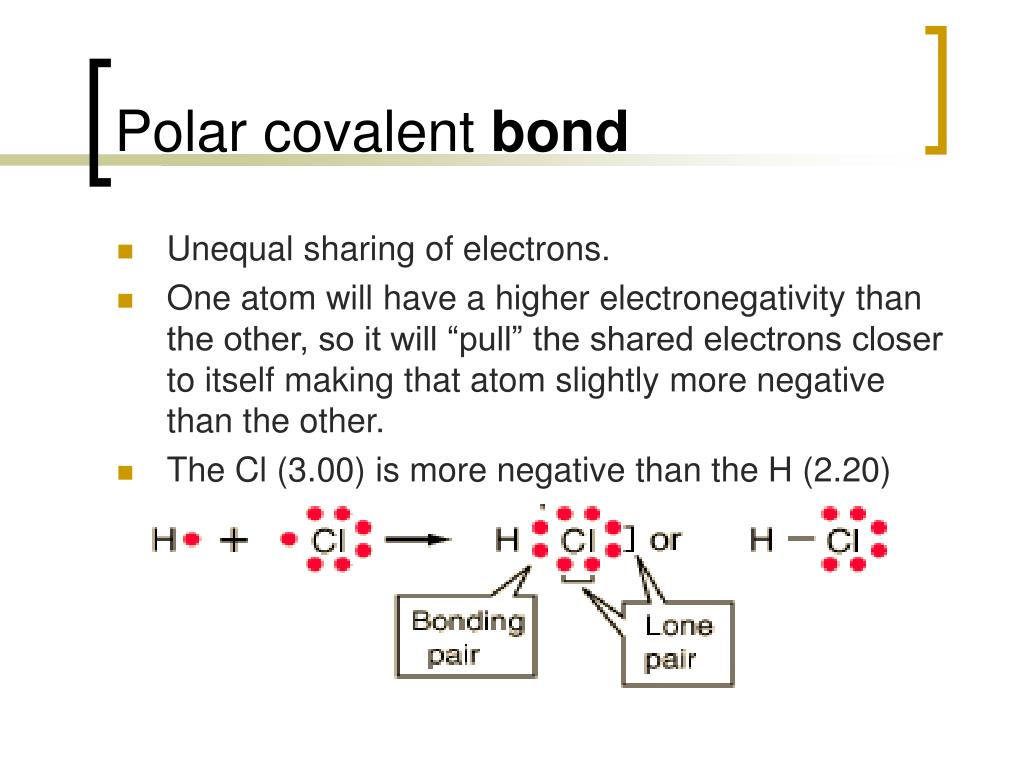
Which Two Atoms Would Typically Form A Covalent Bond - For example, water, (\(\ce{h2o}\)), has two covalent bonds between a single oxygen atom. Fluorine and the other halogens in group 7a (17) have seven valence electrons and can. Web valence bond theory is most often used to describe bonding in organic molecules. When two nonmetal atoms bond, they. Web covalent bonds involve the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. The classification of covalent bonds is done in three ways, depending on the no. The sharing of atoms helps complete the outer shell, or valence shell, of both atoms. A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form. Web two different atoms can also share electrons and form covalent bonds. The number of bonds an element forms in a covalent compound is determined by the number.
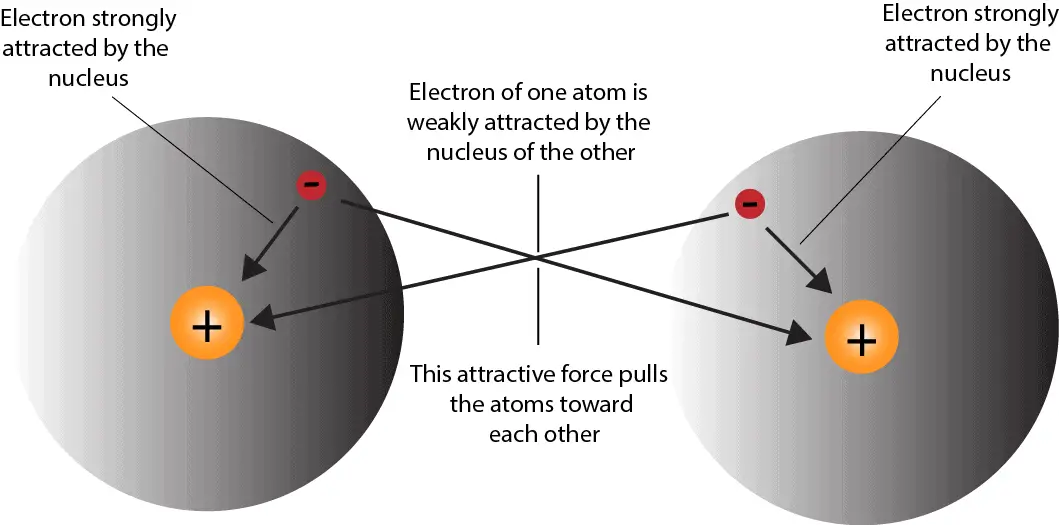
Web the two atoms can share their unpaired electrons to make a covalent bond: Web oxygen and other atoms in group 6a (16) obtain an octet by forming two covalent bonds. Covalent bonds are formed between two. Web covalent bonds involve the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. Web covalent bonds take place between nonmetal elements in the periodic table such as carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. The number of bonds an element forms in a covalent compound is determined by the number. For example, water, (\(\ce{h2o}\)), has two covalent bonds between a single oxygen atom. Electron pairs shared between atoms of equal or very similar electronegativity constitute a nonpolar covalent. Web what two atoms would typically would form a covalent bond? Web atoms can also make chemical bonds by sharing electrons equally between each other.
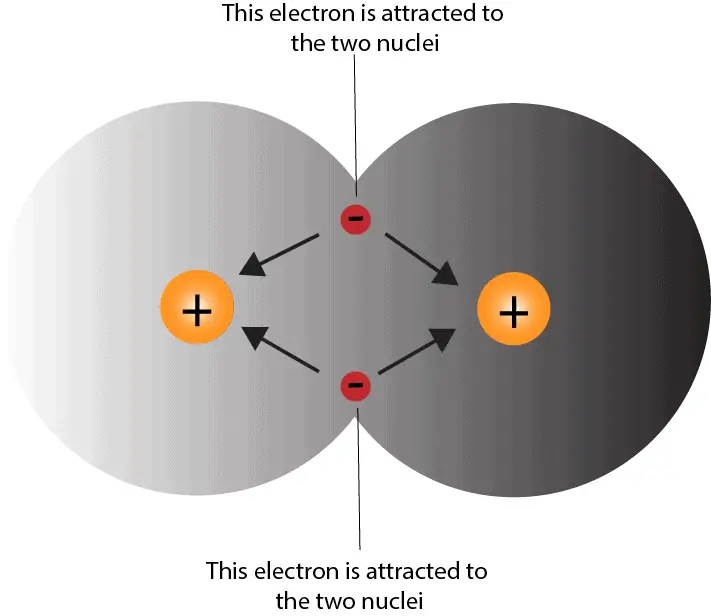
Web a covalent bond is formed between two atoms by sharing electrons. A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form. The classification of covalent bonds is done in three ways, depending on the no. Web a covalent bond forming h 2 (right) where two hydrogen atoms share the two electrons. Fluorine and the other halogens in group 7a (17) have seven valence electrons and can. Web covalent bonds involve the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. Web atoms can also make chemical bonds by sharing electrons equally between each other. Web what two atoms would typically would form a covalent bond? Note that the h atom has a full valence shell with two electrons, while the f atom. Web types of covalent bonds.
Which Pair Of Atoms Forms The Most Polar Bond
Web covalent bonds take place between nonmetal elements in the periodic table such as carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. Web oxygen and other atoms in group 6a (16) obtain an octet by forming two covalent bonds. Covalent bonds are formed between two. Fluorine and the other halogens in group 7a (17) have seven valence electrons and can. In this model,.
How hydrogen atoms share valence electrons to form covalent bond and
Web a covalent bond forming h 2 (right) where two hydrogen atoms share the two electrons. Such bonds are called covalent bonds. Electron pairs shared between atoms of equal or very similar electronegativity constitute a nonpolar covalent. Web what two atoms would typically would form a covalent bond? Web types of covalent bonds.
IGCSE Chemistry 2017 1.44 Know that a Covalent Bond is Formed Between
Web what two atoms would typically would form a covalent bond? Web atoms can also make chemical bonds by sharing electrons equally between each other. Web oxygen and other atoms in group 6a (16) obtain an octet by forming two covalent bonds. Web covalent bonds involve the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. Fluorine and the other halogens in group.
How hydrogen atoms share valence electrons to form covalent bond and
Web what two atoms would typically would form a covalent bond? A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form. Web covalent bonds involve the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. Web a covalent bond is formed between two atoms by sharing electrons. Web the two atoms can share their unpaired electrons to make.
Covalent Bonding (Biology) — Definition & Role Expii
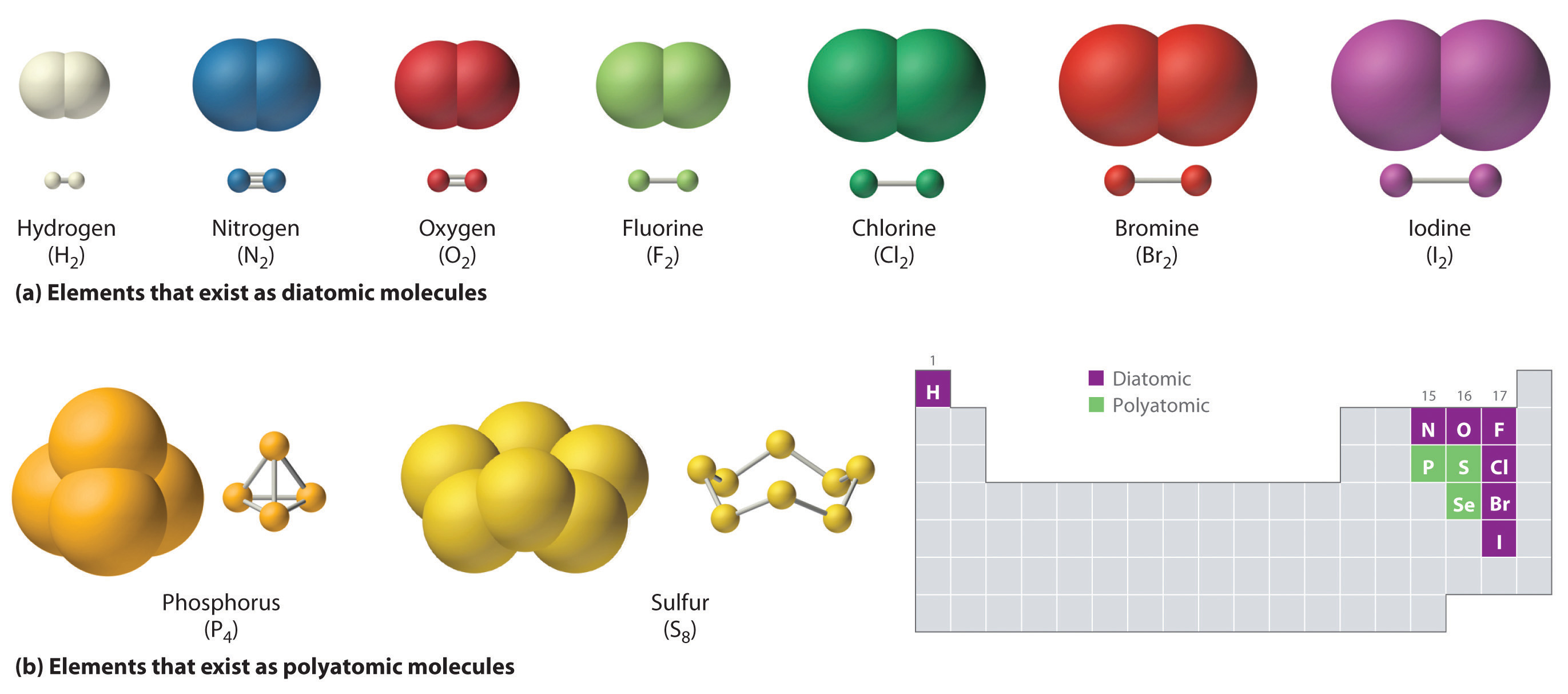
Nonmetals are on the right side of the periodic table. Web covalent bonds involve the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. Web valence bond theory is most often used to describe bonding in organic molecules. Fluorine and the other halogens in group 7a (17) have seven valence electrons and can. Such bonds are called covalent bonds.
CH150 Chapter 4 Covalent Bonds and Molecular Compounds Chemistry
Web the hydrogen atom and the halogen atoms form only one covalent bond to other atoms in stable neutral compounds. Web what two atoms would typically would form a covalent bond? Web a covalent bond forming h 2 (right) where two hydrogen atoms share the two electrons. A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons.
CH150 Chapter 4 Covalent Bonds and Molecular Compounds Chemistry
Fluorine and the other halogens in group 7a (17) have seven valence electrons and can. When two nonmetal atoms bond, they. Web covalent bonds take place between nonmetal elements in the periodic table such as carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. Web a covalent bond forming h 2 (right) where two hydrogen atoms share the two electrons. Web the two atoms.
Atoms, Isotopes, Ions, and Molecules The Building Blocks · Biology
Web covalent bonds take place between nonmetal elements in the periodic table such as carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. The number of bonds an element forms in a covalent compound is determined by the number. A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form. Note that the h atom has a full valence shell.
PPT Notes 53 Covalent Bonds PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Web covalent bonds involve the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. The number of bonds an element forms in a covalent compound is determined by the number. The sharing of atoms helps complete the outer shell, or valence shell, of both atoms. Web two different atoms can also share electrons and form covalent bonds. Fluorine and the other halogens in.
Chapter 5.6 Properties of Polar Covalent Bonds Chemistry LibreTexts
Web a covalent bond is a bond where two or more atoms share electrons. Web types of covalent bonds. Web valence bond theory is most often used to describe bonding in organic molecules. However, the carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms can bond. When two nonmetal atoms bond, they.
Note That The H Atom Has A Full Valence Shell With Two Electrons, While The F Atom.
Fluorine and the other halogens in group 7a (17) have seven valence electrons and can. Web a covalent bond is a bond where two or more atoms share electrons. Web types of covalent bonds. Web atoms can also make chemical bonds by sharing electrons equally between each other.
Web Valence Bond Theory Is Most Often Used To Describe Bonding In Organic Molecules.
Covalent bonds are formed between two. In this model, covalent bonds are considered to form from the overlap of. However, the carbon, oxygen, and nitrogen atoms can bond. Web oxygen and other atoms in group 6a (16) obtain an octet by forming two covalent bonds.
When Two Nonmetal Atoms Bond, They.
Web what two atoms would typically would form a covalent bond? Web the two atoms can share their unpaired electrons to make a covalent bond: Such bonds are called covalent bonds. Electron pairs shared between atoms of equal or very similar electronegativity constitute a nonpolar covalent.
Web A Covalent Bond Forming H 2 (Right) Where Two Hydrogen Atoms Share The Two Electrons.
Web the hydrogen atom and the halogen atoms form only one covalent bond to other atoms in stable neutral compounds. The number of bonds an element forms in a covalent compound is determined by the number. Web covalent bonds take place between nonmetal elements in the periodic table such as carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. Web covalent bonds involve the sharing of electron pairs between atoms.