What Type Of Atoms Form Covalent Bonds
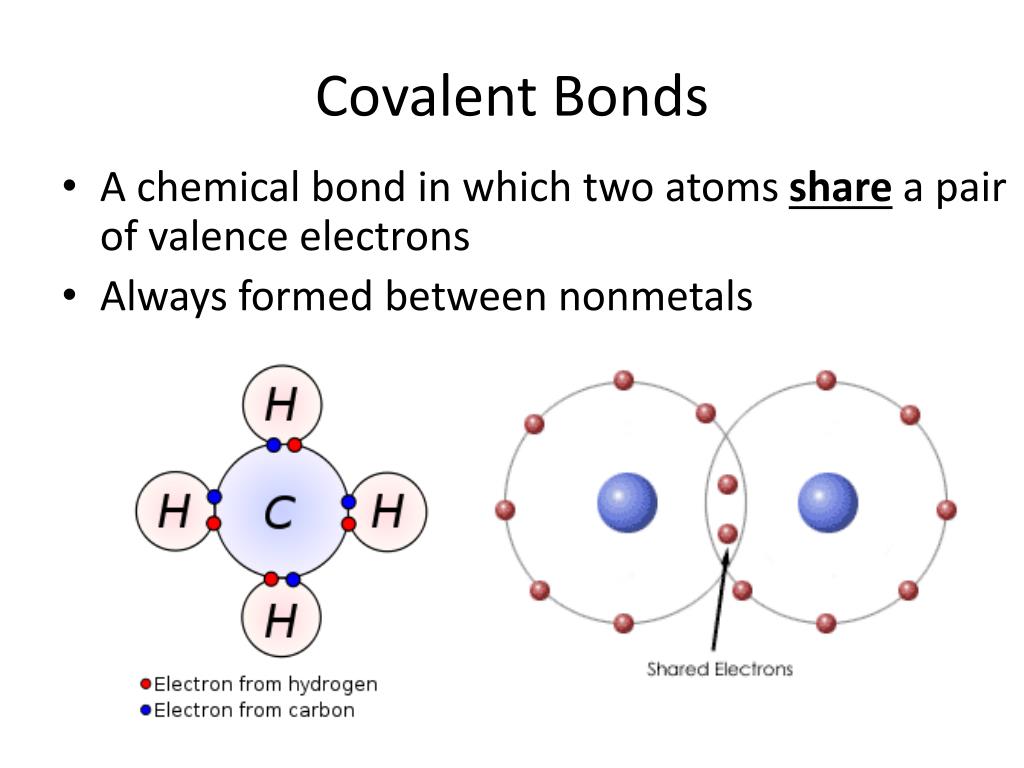
What Type Of Atoms Form Covalent Bonds - Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms. Various methods of showing a covalent bond. Group 6a form 2 bonds; Web typically, the atoms of group 4a form 4 covalent bonds; These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. Lewis dot structures are one way to represent how atoms form covalent bonds. Web the octet rule can be satisfied by the sharing of electrons between atoms to form covalent bonds. And group 7a form one bond. A triple bond is formed when three pairs of electrons are shared between the two participating atoms. Web compounds can be covalent or ionic.
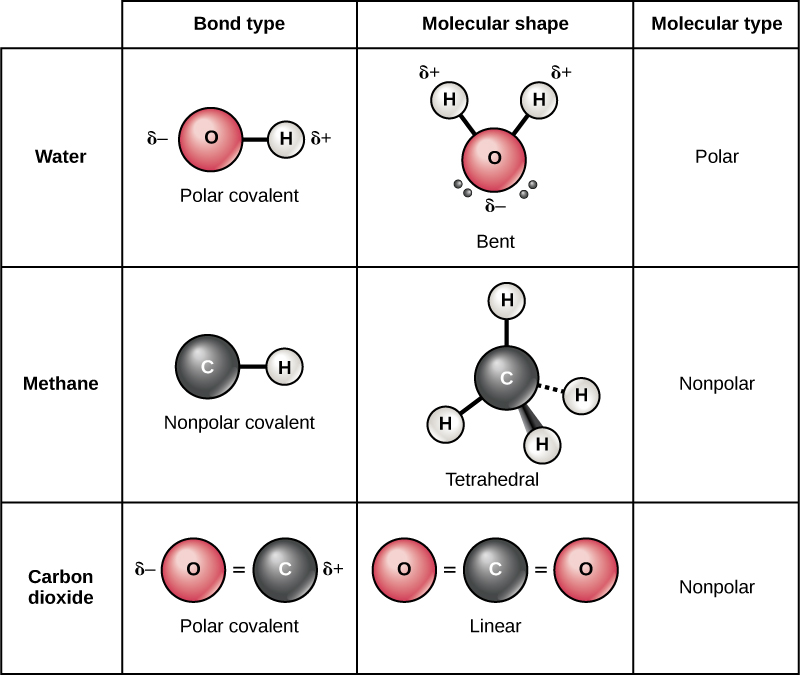
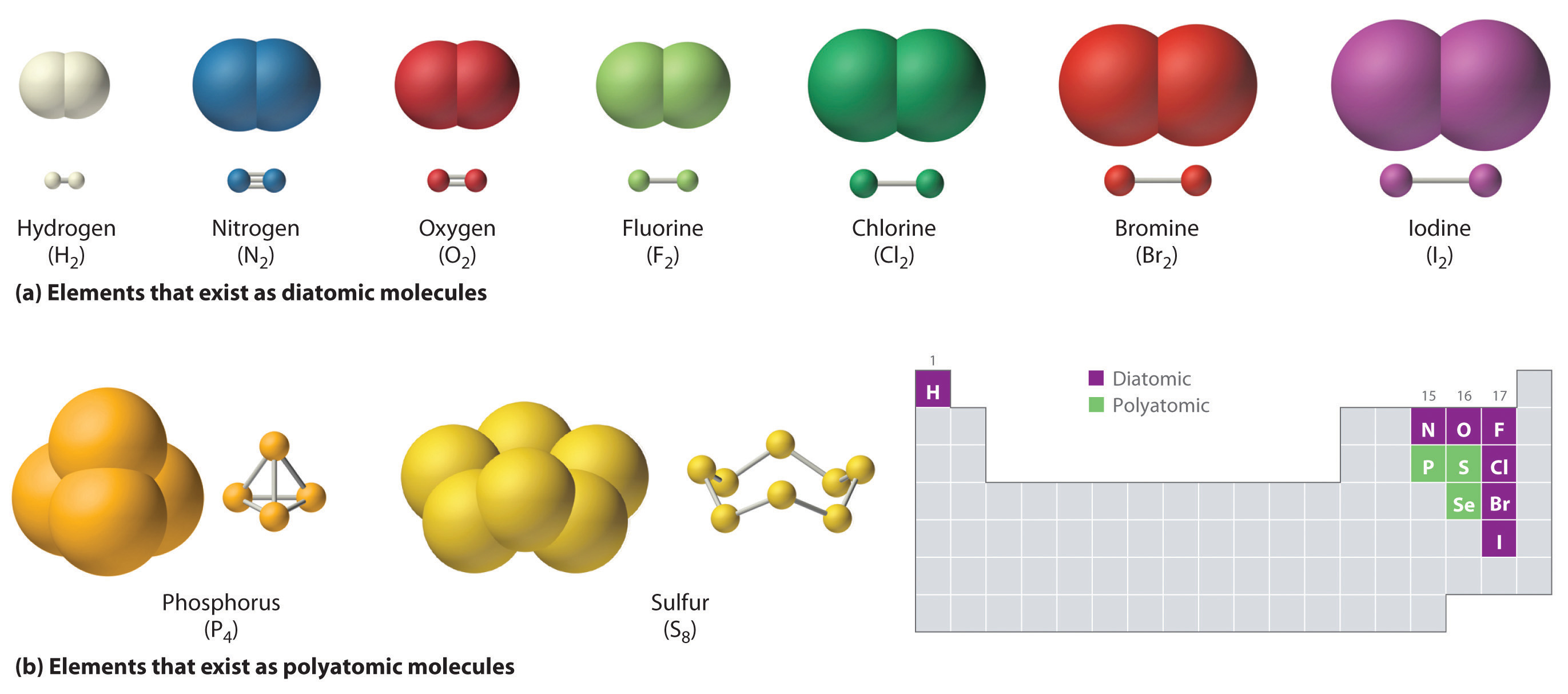
Molecules of identical atoms, such as h 2 and buckminsterfullerene (c 60 ), are also held together by covalent bonds. Web covalent compounds are basically the molecules that form when two different atoms form a covalent bond. Web as a general rule, covalent bonds are formed between elements lying toward the right in the periodic table (i.e., the nonmetals). Web covalent bonds involve the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. Web covalent bonding is the type of bond that holds together the atoms within a polyatomic ion. Web a covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. For example, in hi it is about 5%, but in hf. The electrons involved are in the outer shells of the atoms. Web typically, the atoms of group 4a form 4 covalent bonds; Covalent bonds form between atoms of nonmetallic elements.
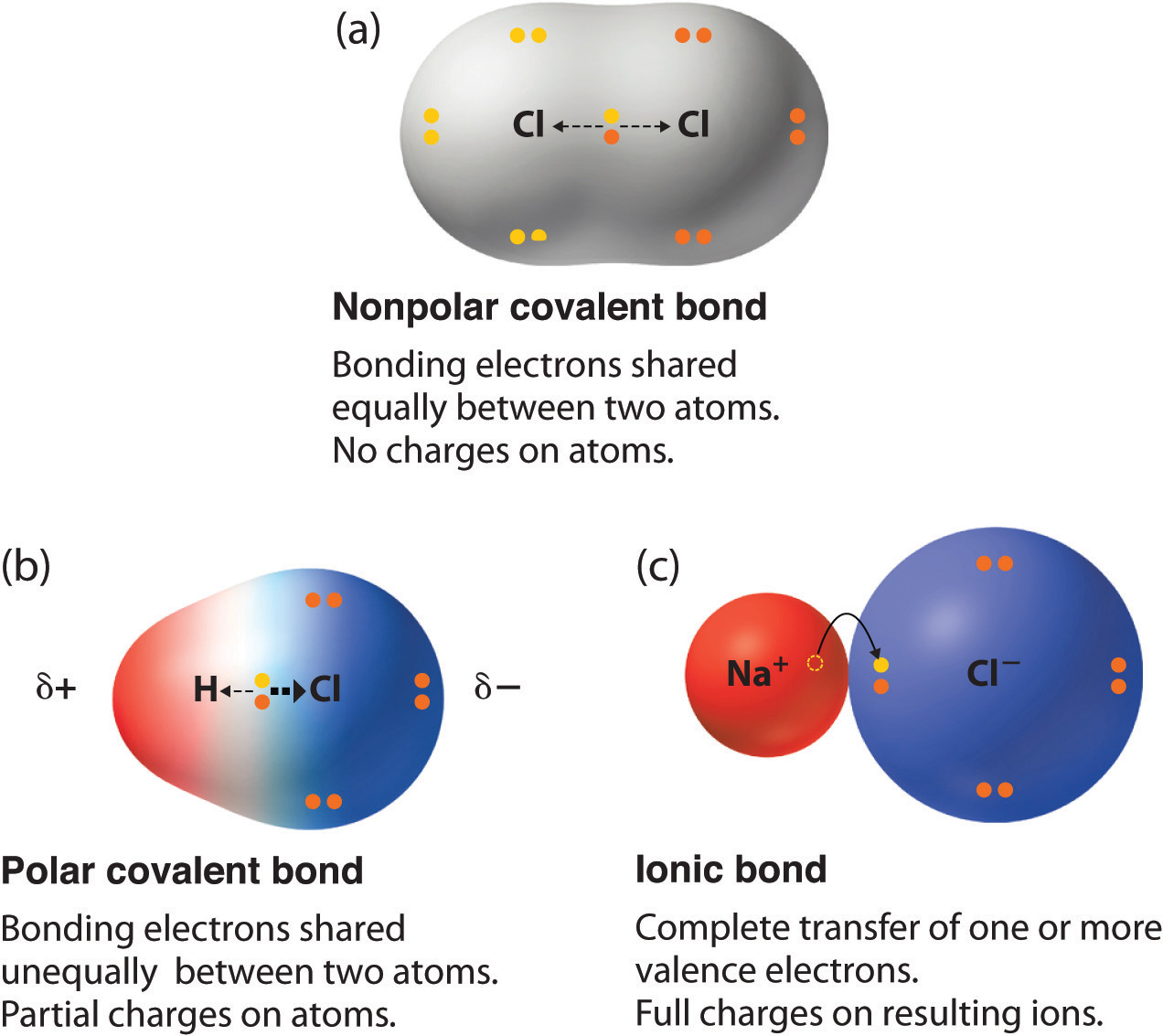
Atoms will covalently bond with other atoms in order to gain more stability, which is gained by forming a full electron shell. Web covalent bonds involve the sharing of electron pairs between atoms. Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms. The differences between ionic and covalent bonds are explained by the use of scientific models and examples from nature. These bonds are stronger and much more common than are ionic bonds in the molecules of living organisms. On the basis of the number of electrons shared covalent bonds are of three types. In general, bonds are considered to be covalent if the electronegativity difference between the two atoms bonding is less than 2.0 pauling units. Web covalent bonds form between atoms with relatively high electron affinity and they form individual, separate molecules (figure below). Web the hydrogen atom and the halogen atoms form only one covalent bond to other atoms in stable neutral compounds. Web typically, the atoms of group 4a form 4 covalent bonds;
covalent bond Definition, Properties, Examples, & Facts Britannica
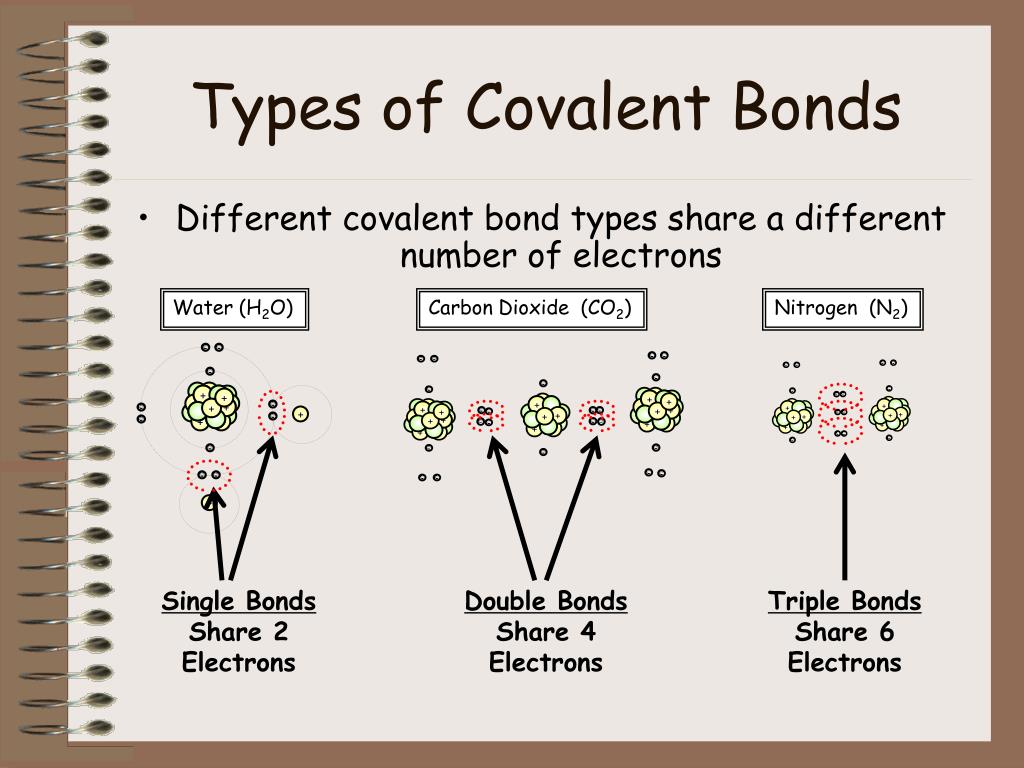
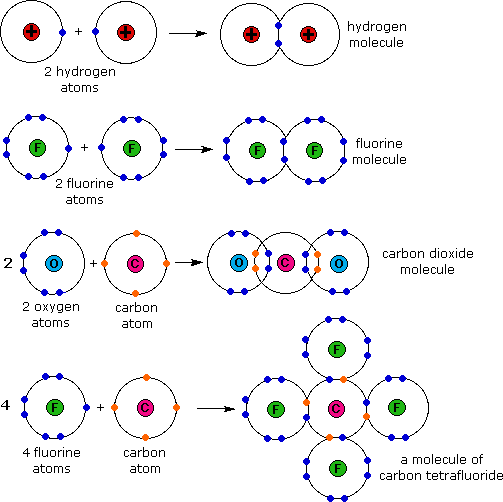
Web the two atoms can also share two pairs of electrons (a double bond) or three pairs of electrons (triple bond): Covalent bonds form between atoms of nonmetallic elements. In general, bonds are considered to be covalent if the electronegativity difference between the two atoms bonding is less than 2.0 pauling units. If one electron pair is shared between two.
Covalent Bonds Biology for NonMajors I
If one electron pair is shared between two elements they form a single covalent bond. This is summarized in the table below. Various methods of showing a covalent bond. Web formation of covalent bonds. Web covalent bonds are formed by sharing of electrons between two atoms.
CH150 Chapter 4 Covalent Bonds and Molecular Compounds Chemistry
This is summarized in the table below. Web oxygen and other atoms in group 6a (16) obtain an octet by forming two covalent bonds. In general, bonds are considered to be covalent if the electronegativity difference between the two atoms bonding is less than 2.0 pauling units. Molecules of identical atoms, such as h 2 and buckminsterfullerene (c 60 ),.
Covalent Bonding (Biology) — Definition & Role Expii
A table of lewis dot symbols of nonmetal elements that form covalent bonds is shown in fig. Web covalent bonds last updated jan 29, 2023 covalent bonding covalent bonds vs ionic bonds covalent bonding occurs when pairs of electrons are shared by atoms. A triple bond is formed when three pairs of electrons are shared between the two participating atoms..
PPT Notes 53 Covalent Bonds PowerPoint Presentation, free download
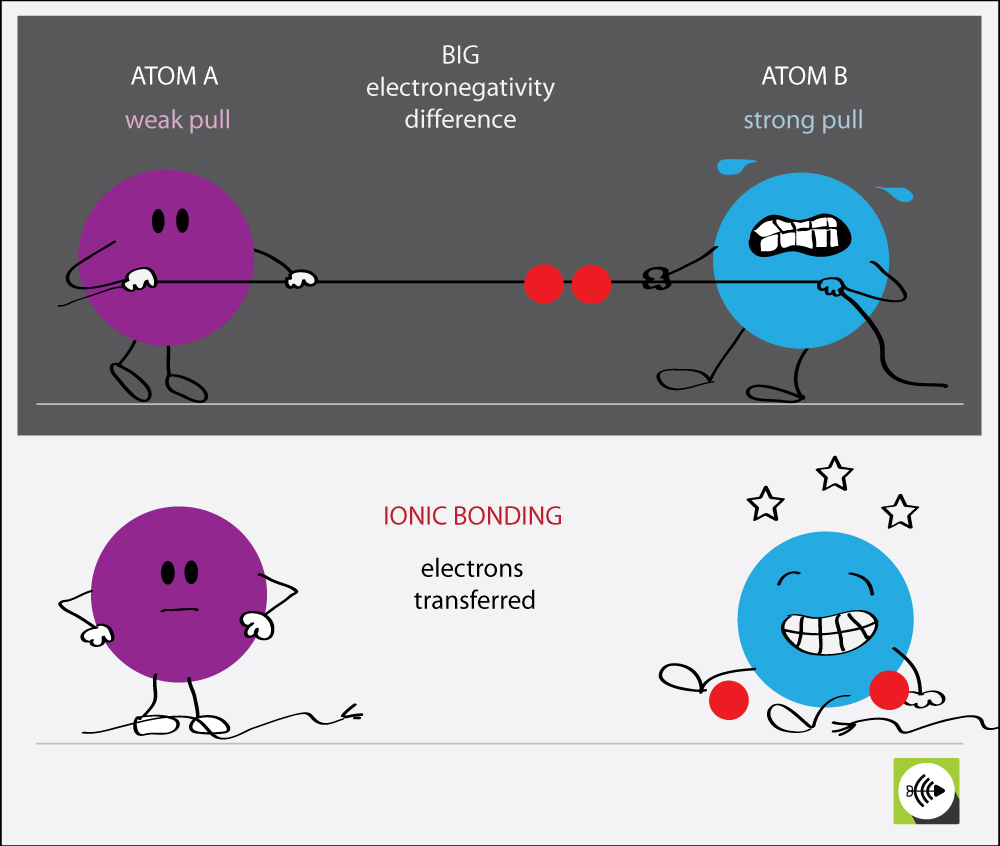
It is a type of chemical bond that generates two oppositely charged ions. Web in the structure there are two oxygen atoms and one carbon atom which are bonded covalently. Web the octet rule can be satisfied by the sharing of electrons between atoms to form covalent bonds. Lewis dot structures are one way to represent how atoms form covalent.
Electronegativity Bond Scale Surfguppy Chemistry made easy for
Web formation of covalent bonds. For example, in hi it is about 5%, but in hf. Atoms will covalently bond with other atoms in order to gain more stability, which is gained by forming a full electron shell. Web covalent bonding is the type of bond that holds together the atoms within a polyatomic ion. Fluorine and the other halogens.
PPT Covalent Bonds PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6647183
The electrons involved are in the outer shells of the atoms. An example of a covalent compound is ammonia. Web the two atoms can also share two pairs of electrons (a double bond) or three pairs of electrons (triple bond): Web covalent bonds form between atoms with relatively high electron affinity and they form individual, separate molecules (figure below). The.
EduMission Chemistry Form 4 Chapter 5 Covalent Bond
Web oxygen and other atoms in group 6a (16) obtain an octet by forming two covalent bonds. And group 7a form one bond. Web there are actually three different types of chemical bonds, called covalent, ionic, and metallic bonds. Group 6a form 2 bonds; The number of bonds that an atom can form can often be predicted from the number.
Chapter 5.6 Properties of Polar Covalent Bonds Chemistry LibreTexts
Web as a general rule, covalent bonds are formed between elements lying toward the right in the periodic table (i.e., the nonmetals). Group 5a form 3 bonds; A covalent bond is the force of attraction that holds together two nonmetal atoms that share a pair of electrons. The number of bonds that an atom can form can often be predicted.
Covalent Bond Biology Dictionary
Molecules of identical atoms, such as h 2 and buckminsterfullerene (c 60 ), are also held together by covalent bonds. In ionic bonds, the metal loses electrons to become a positively charged cation, whereas the nonmetal accepts those electrons to become a negatively charged anion. Web covalent compounds are basically the molecules that form when two different atoms form a.
Fluorine And The Other Halogens In Group 7A (17) Have Seven Valence Electrons And Can Obtain An Octet By Forming One Covalent Bond.
Some compounds contain both covalent and ionic bonds. Group 5a form 3 bonds; Web a covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. In ionic bonds, the metal loses electrons to become a positively charged cation, whereas the nonmetal accepts those electrons to become a negatively charged anion.
Various Methods Of Showing A Covalent Bond.
Also known as an electrovalent bond, it is a type of bond formed from the strong electrostatic force of attraction between oppositely. If one electron pair is shared between two elements they form a single covalent bond. Web oxygen and other atoms in group 6a (16) obtain an octet by forming two covalent bonds. Web covalent bonds are formed by sharing of electrons between two atoms.
These Electron Pairs Are Known As Shared Pairs Or Bonding Pairs.
It is a type of chemical bond that generates two oppositely charged ions. Covalent bonds form between atoms of nonmetallic elements. Nonmetal atoms frequently form covalent bonds with other nonmetal atoms. An example of a covalent compound is ammonia.
This Is Especially True Of The Nonmetals Of The Second Period Of The Periodic Table (C, N, O, And F).
Web in the structure there are two oxygen atoms and one carbon atom which are bonded covalently. Group 6a form 2 bonds; Each atom contributes one electron to the shared pair, helping both atoms achieve an octet in their valence shell. These bonds are stronger and much more common than are ionic bonds in the molecules of living organisms.