Template Strand Vs Non Template Strand
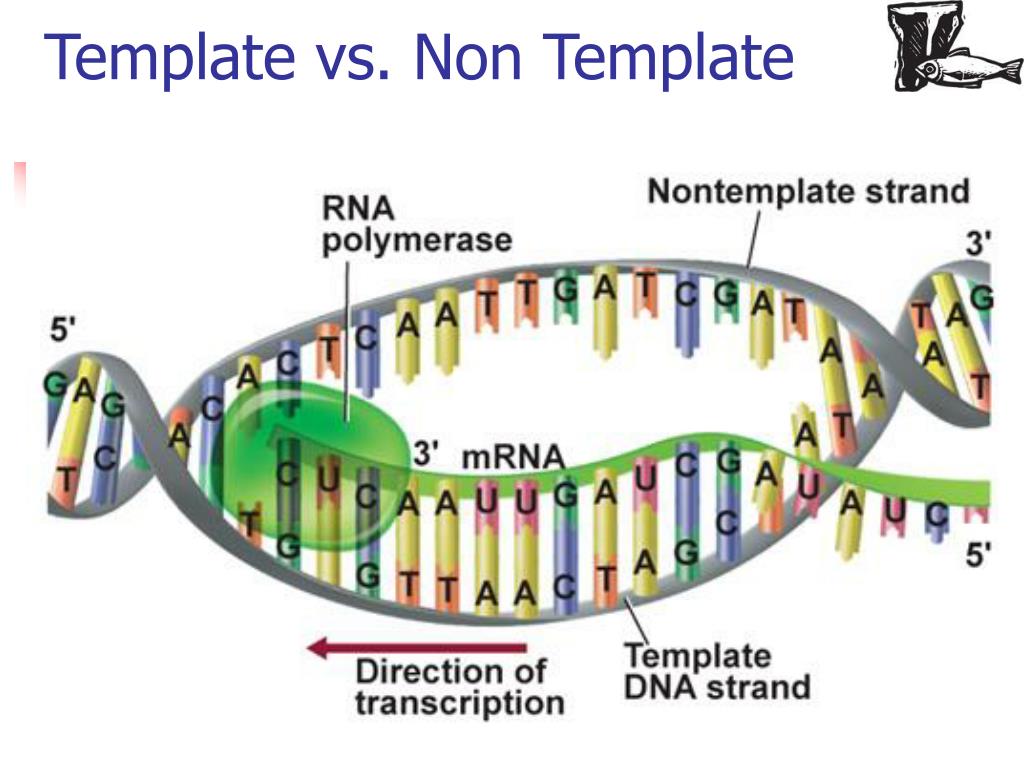
Template Strand Vs Non Template Strand - The template strand and the. A dna template strand generally refers to the strand which is used by the enzyme dna polymerases and rna polymerases to attach with the complementary bases during the process of replication of dna or at the time of transcription of rna respectively. Web this template strand is called the noncoding strand. Web it is presented in the 5' to 3' direction. Template strand is directed in the 5’ to 3’ direction. It is synthesized in fragments. The lagging strand is the dna strand replicated in the 3′ to 5′ direction during dna replication from a template strand. The template strand is the one that rna polymerase uses as the basis to build the rna. Antisense strand or minus strand: The direction of the template strand is in 3’ to 5’, whereas the coding strand shows opposite directional polarity, i.e.
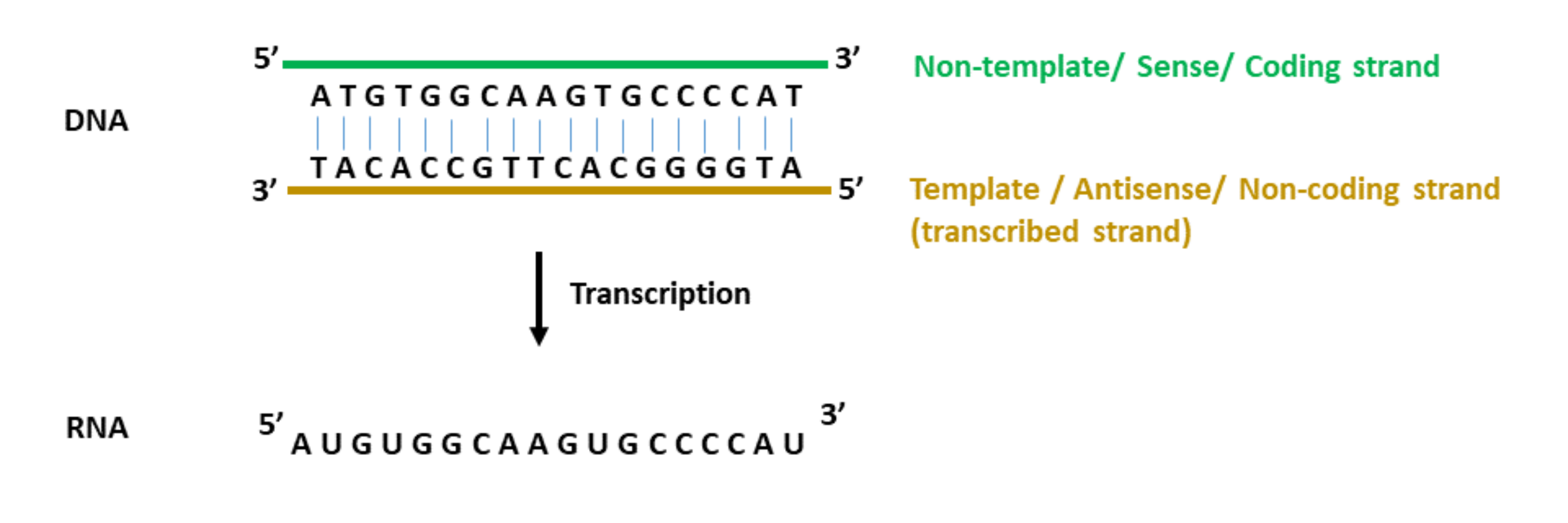
Web july 21, 2021 6 mins read what is dna template strand? The template strand is the one that rna polymerase uses as the basis to build the rna. Wherever a gene exists on a dna molecule, one strand is the coding strand (or sense strand ), and the other is the noncoding strand (also called the antisense strand, [3] anticoding strand, template strand or transcribed strand ). This template strand is called the noncoding strand. Antisense strand or minus strand: Coding strand of dna (sense strand) has the same sequences as transcribed rna, except for having thymine in place of rna’s uracil. What is meant by the template vs. The direction of the template strand is in 3’ to 5’, whereas the coding strand shows opposite directional polarity, i.e. Web depending on the context, sense may have slightly different meanings. This strand is called the template strand.
Is the leading strand 5 to 3? Web by perrine juillion / july 2, 2019. This template strand is called the noncoding strand. The template strand is the one that rna polymerase uses as the basis to build the rna. Antisense strand or minus strand: Web this template strand is called the noncoding strand. Template strand is directed in the 5’ to 3’ direction. The coding strand serves as a template for producing complementary rna. The coding strand has the same nucleotide sequence as mrna except that. Web in this mcat question of the day, we will be taking a look at the key differences between the template strand and the coding/sense strand.
WiFi Boosters, Repeaters and Range Extenders A Deep Dive
This strand is also called the coding. Coding strand is also called a template strand which gets transcribed to rna. The nontemplate strand is referred to as the coding strand because its sequence will be the same as that of the new rna molecule. Is the leading strand 5 to 3? The rna product is complementary to the template strand.
Which of the Following Is the Template for Transcription AlizahasClarke
Web the nontemplate strand is referred to as the coding strand because its sequence will be the same as that of the new rna molecule. Wherever a gene exists on a dna molecule, one strand is the coding strand (or sense strand ), and the other is the noncoding strand (also called the antisense strand, [3] anticoding strand, template strand.
Coding Strand of DNA bartleby
Web dna template strand and the creation of its complementary strand the primary enzyme involved in this is dna polymerase which joins nucleotides to synthesize the new complementary strand. Web this template strand is called the noncoding strand. The direction of the template strand is in 3’ to 5’, whereas the coding strand shows opposite directional polarity, i.e. Wherever a.
Template vs. Nontemplate (Noncoding vs. Coding strand of DNA) YouTube
Wherever a gene exists on a dna molecule, one strand is the coding strand (or sense strand ), and the other is the noncoding strand (also called the antisense strand, [3] anticoding strand, template strand or transcribed strand ). The lagging strand is the dna strand replicated in the 3′ to 5′ direction during dna replication from a template strand..
Difference Between Template and Coding Strand
The template strand and the. It is synthesized in fragments. The lagging strand is the dna strand replicated in the 3′ to 5′ direction during dna replication from a template strand. The template strand is the one that rna polymerase uses as the basis to build the rna. This template strand is called the noncoding strand.
Coding NonCoding Sense Antisense Template and NonTemplate Strands
What is meant by the template vs. Web biology questions and answers. The direction of the template strand is in 3’ to 5’, whereas the coding strand shows opposite directional polarity, i.e. Web depending on the context, sense may have slightly different meanings. Dna polymerase also proofreads each new dna strand to make sure that there are no errors.
Common misconceptions in biology Making sense of the sense and
The term template strand refers to the dna sequence that can duplicate itself during mrna synthesis. Web depending on the context, sense may have slightly different meanings. Web transcription uses one of the two exposed dna strands as a template; This strand is called the template strand. The nontemplate strand is referred to as the coding strand because its sequence.
Difference between Sense Strand and Antisense Strand of DNA Dna
Coding strand of dna (sense strand) has the same sequences as transcribed rna, except for having thymine in place of rna’s uracil. The lagging strand is the dna strand replicated in the 3′ to 5′ direction during dna replication from a template strand. Antisense strand or minus strand: The nontemplate strand is referred to as the coding strand because its.
The coding strand of DNA is 5'AATTCAAATTAGG3'
A dna template strand generally refers to the strand which is used by the enzyme dna polymerases and rna polymerases to attach with the complementary bases during the process of replication of dna or at the time of transcription of rna respectively. The copy of the template strand is read by ribosomes, which then produce a. Web dna template strand.
Template And Nontemplate Strand Flyer Template
Web july 21, 2021 6 mins read what is dna template strand? This strand is also called the coding. Coding strand of dna (sense strand) has the same sequences as transcribed rna, except for having thymine in place of rna’s uracil. Web depending on the context, sense may have slightly different meanings. What is meant by the template vs.
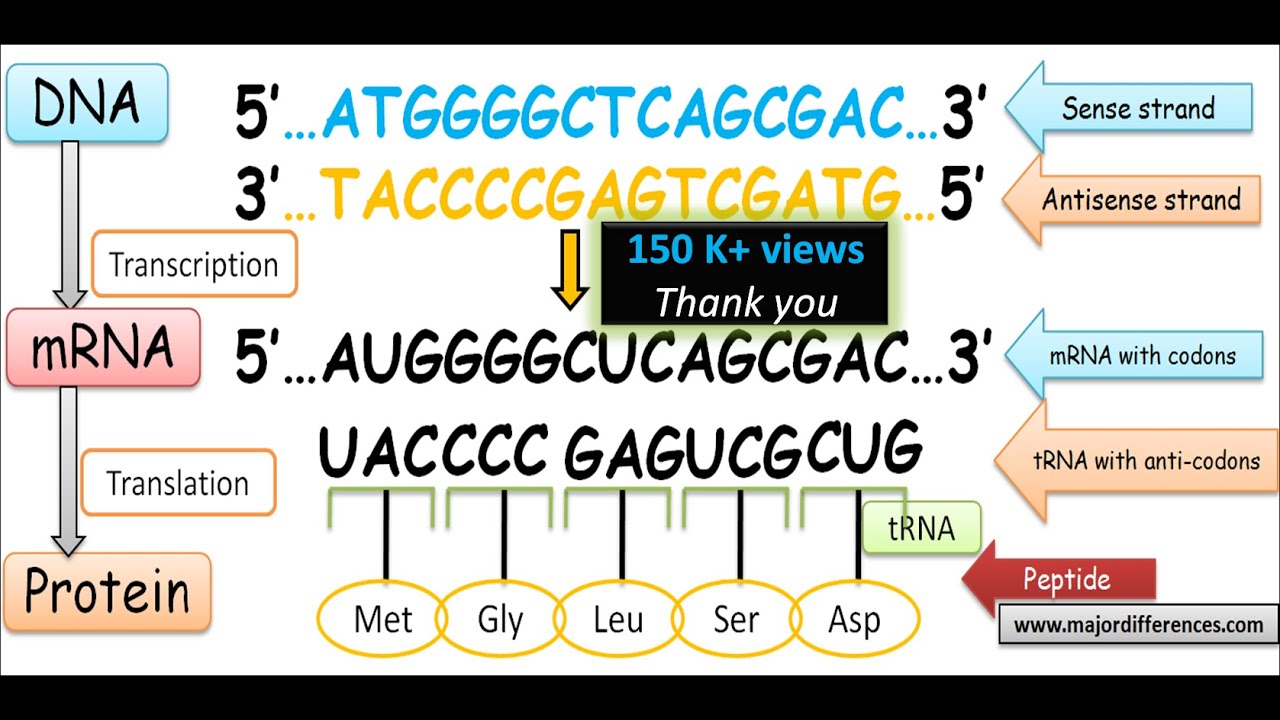
Web In This Mcat Question Of The Day, We Will Be Taking A Look At The Key Differences Between The Template Strand And The Coding/Sense Strand.
Web biology questions and answers. What is meant by the template vs. Is the leading strand 5 to 3? Web transcription uses one of the two exposed dna strands as a template;
The Coding Strand Functions To Determine The Correct Nucleotide Base Sequence Of The Rna Strand.
The template strand is the side of the dna molecule that stores the information to be transcribed into mrna. The template strand and the. What is meant by the template vs. The direction of the template strand is in 3’ to 5’, whereas the coding strand shows opposite directional polarity, i.e.
This Template Strand Is Called The Noncoding Strand.
In most organisms, the strand of dna that serves as the template for one gene may be the nontemplate strand for other genes within the same chromosome. The nontemplate strand is referred to as the coding strand because its sequence will be the same as that of the new rna molecule. Is the lagging strand the template strand? Web dna template strand and the creation of its complementary strand the primary enzyme involved in this is dna polymerase which joins nucleotides to synthesize the new complementary strand.
Template Strand Is Directed In The 5’ To 3’ Direction.
Web this template strand is called the noncoding strand. A dna template strand generally refers to the strand which is used by the enzyme dna polymerases and rna polymerases to attach with the complementary bases during the process of replication of dna or at the time of transcription of rna respectively. This strand is also called the coding. Dna polymerase also proofreads each new dna strand to make sure that there are no errors.