Statistics And Probability Cheat Sheet
Statistics And Probability Cheat Sheet - A bmeans that ais less than or the same as b. (iv) pa a = p a. Cheat sheet algebra (i) a+z b a b = z (ii) a(b+ c) = a b+ a c. Web successfully working your way through probability problems means understanding some basic rules of probability along with discrete and continuous probability distributions. Web chebyshev's inequality let $x$ be a random variable with expected value $\mu$. For $k, \sigma>0$, we have the following inequality: (iii) p1 ab = p1 a p1 b. Material based on joe blitzstein's. 22 mean of a discrete probability distribution: [ ( )] standard deviation of a probability distribution:
Material based on joe blitzstein's. (v) abmeans ais bigger than b. Web sheets interchange “r” and “x” for number of successes chapter 5 discrete probability distributions: Web successfully working your way through probability problems means understanding some basic rules of probability along with discrete and continuous probability distributions. (iii) p1 ab = p1 a p1 b. 22 mean of a discrete probability distribution: Web chebyshev's inequality let $x$ be a random variable with expected value $\mu$. A bmeans that ais less than or the same as b. For $k, \sigma>0$, we have the following inequality: Cheat sheet algebra (i) a+z b a b = z (ii) a(b+ c) = a b+ a c.
Material based on joe blitzstein's. (iv) pa a = p a. For $k, \sigma>0$, we have the following inequality: 22 mean of a discrete probability distribution: [ ( )] standard deviation of a probability distribution: (iii) p1 ab = p1 a p1 b. Web successfully working your way through probability problems means understanding some basic rules of probability along with discrete and continuous probability distributions. Web chebyshev's inequality let $x$ be a random variable with expected value $\mu$. Cheat sheet algebra (i) a+z b a b = z (ii) a(b+ c) = a b+ a c. A bmeans that ais less than or the same as b.
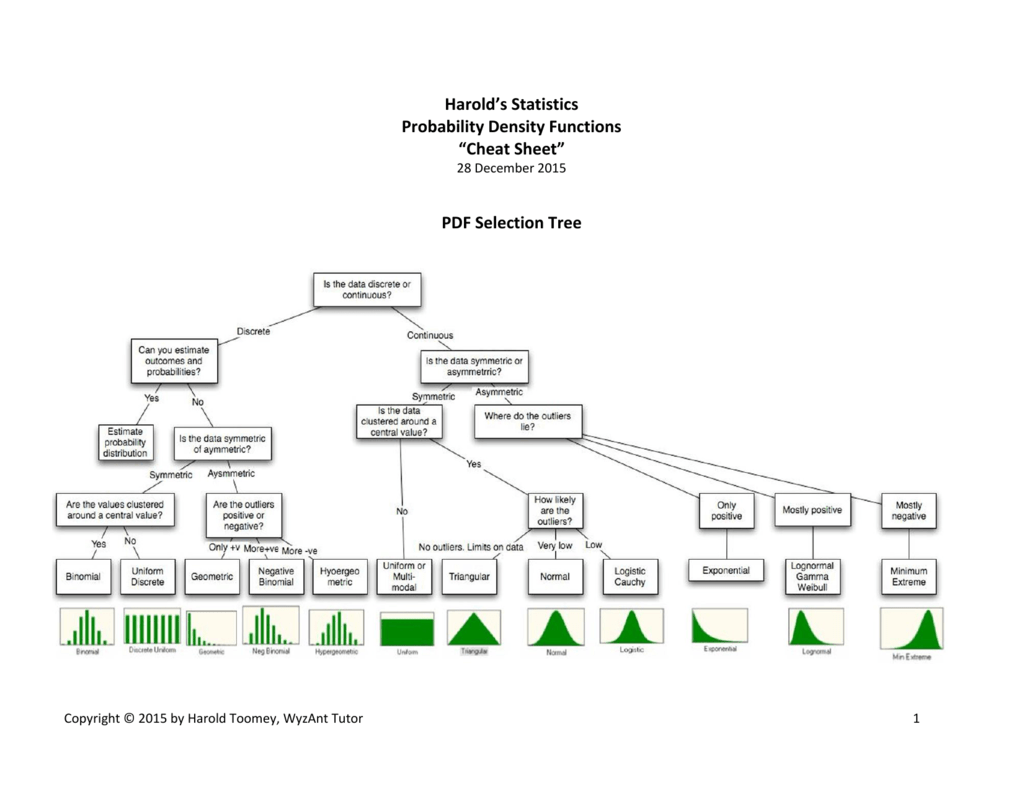
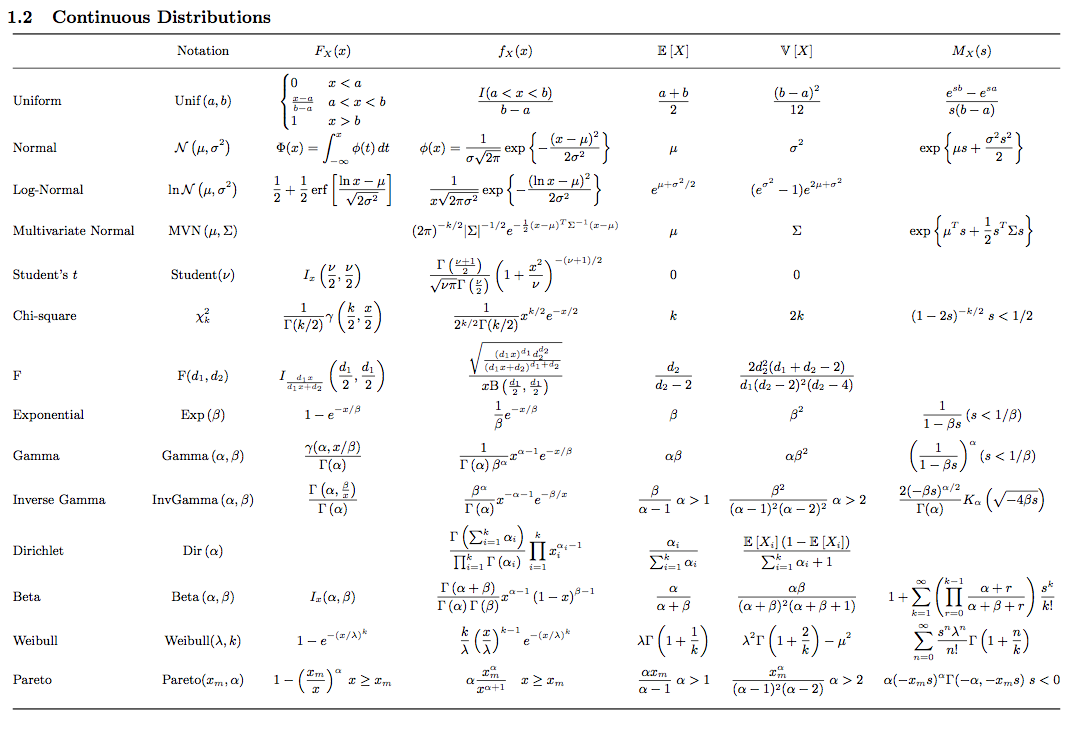
Harold's Statistics PDFs Cheat Sheet
(v) abmeans ais bigger than b. [ ( )] standard deviation of a probability distribution: (iii) p1 ab = p1 a p1 b. For $k, \sigma>0$, we have the following inequality: 22 mean of a discrete probability distribution:
Stats Cheatsheet — Claire SaintDonat
For $k, \sigma>0$, we have the following inequality: 22 mean of a discrete probability distribution: A bmeans that ais less than or the same as b. (v) abmeans ais bigger than b. (iv) pa a = p a.
Probability Rules Cheat Sheet. Basic probability rules with examples
22 mean of a discrete probability distribution: (iii) p1 ab = p1 a p1 b. Web sheets interchange “r” and “x” for number of successes chapter 5 discrete probability distributions: A bmeans that ais less than or the same as b. Web chebyshev's inequality let $x$ be a random variable with expected value $\mu$.
Matthias Vallentin Probability and Statistics Cheat Sheet
(v) abmeans ais bigger than b. Web successfully working your way through probability problems means understanding some basic rules of probability along with discrete and continuous probability distributions. [ ( )] standard deviation of a probability distribution: Web chebyshev's inequality let $x$ be a random variable with expected value $\mu$. 22 mean of a discrete probability distribution:
GitHub wzchen/probability_cheatsheet A comprehensive 10page
(v) abmeans ais bigger than b. For $k, \sigma>0$, we have the following inequality: (iv) pa a = p a. Material based on joe blitzstein's. Web chebyshev's inequality let $x$ be a random variable with expected value $\mu$.
GitHub wzchen/probability_cheatsheet A comprehensive 10page
22 mean of a discrete probability distribution: (iii) p1 ab = p1 a p1 b. Material based on joe blitzstein's. Web sheets interchange “r” and “x” for number of successes chapter 5 discrete probability distributions: For $k, \sigma>0$, we have the following inequality:
QSStatistics1.jpg (1275×1650) Statistics math, Data science
(iv) pa a = p a. (v) abmeans ais bigger than b. For $k, \sigma>0$, we have the following inequality: Web successfully working your way through probability problems means understanding some basic rules of probability along with discrete and continuous probability distributions. Web sheets interchange “r” and “x” for number of successes chapter 5 discrete probability distributions:
Probability For Dummies Cheat Sheet For Dummies Statistics math
Web successfully working your way through probability problems means understanding some basic rules of probability along with discrete and continuous probability distributions. [ ( )] standard deviation of a probability distribution: (iv) pa a = p a. A bmeans that ais less than or the same as b. Material based on joe blitzstein's.
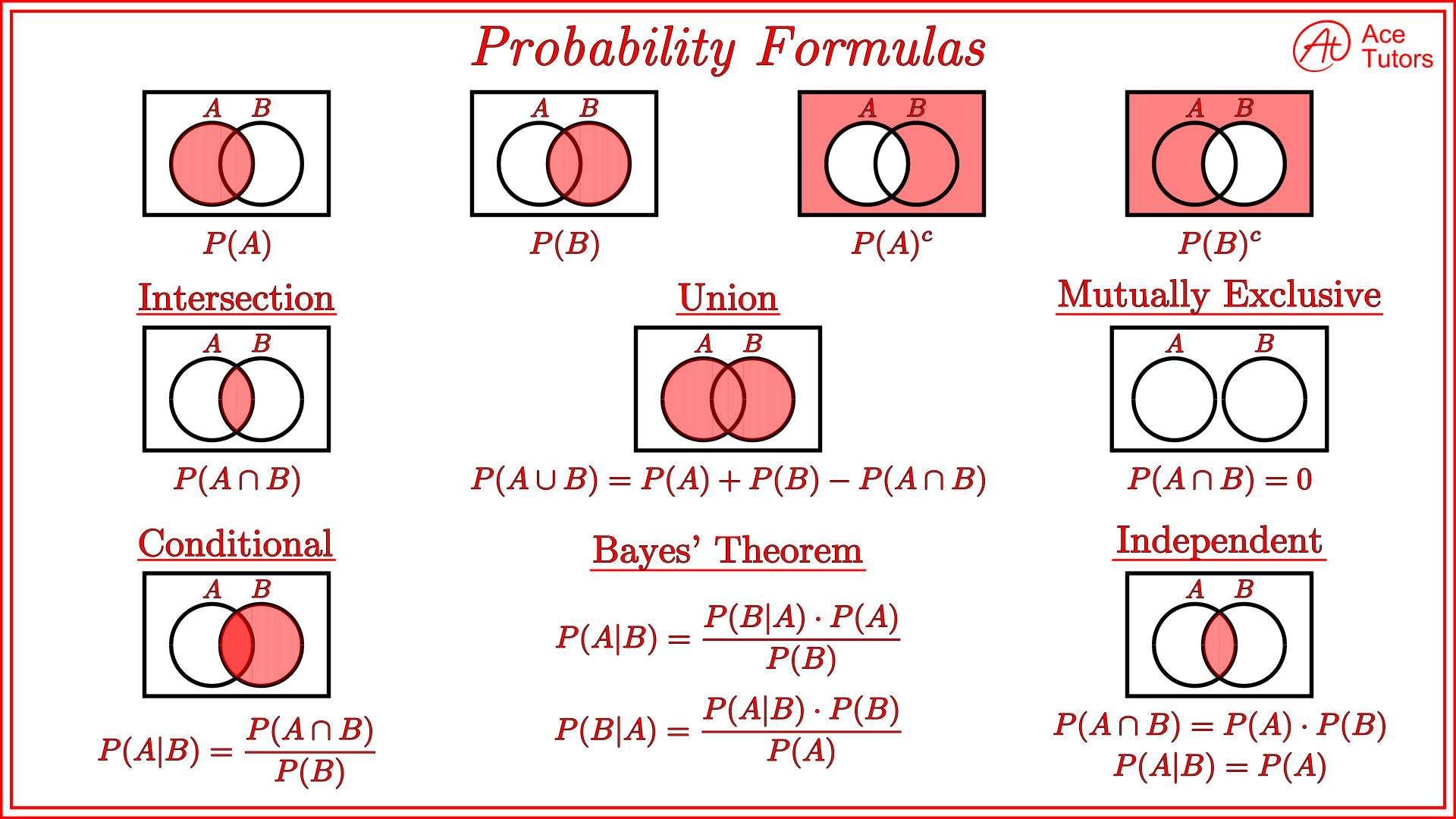
Probability Formula Cheat Sheet Statistics Ace Tutors Blog
Material based on joe blitzstein's. For $k, \sigma>0$, we have the following inequality: (iii) p1 ab = p1 a p1 b. Web successfully working your way through probability problems means understanding some basic rules of probability along with discrete and continuous probability distributions. (iv) pa a = p a.
Statistics Cheat Sheet
Web successfully working your way through probability problems means understanding some basic rules of probability along with discrete and continuous probability distributions. Web sheets interchange “r” and “x” for number of successes chapter 5 discrete probability distributions: Cheat sheet algebra (i) a+z b a b = z (ii) a(b+ c) = a b+ a c. For $k, \sigma>0$, we have.
Web Successfully Working Your Way Through Probability Problems Means Understanding Some Basic Rules Of Probability Along With Discrete And Continuous Probability Distributions.
A bmeans that ais less than or the same as b. Web chebyshev's inequality let $x$ be a random variable with expected value $\mu$. Web sheets interchange “r” and “x” for number of successes chapter 5 discrete probability distributions: (v) abmeans ais bigger than b.
Material Based On Joe Blitzstein's.
[ ( )] standard deviation of a probability distribution: 22 mean of a discrete probability distribution: For $k, \sigma>0$, we have the following inequality: Cheat sheet algebra (i) a+z b a b = z (ii) a(b+ c) = a b+ a c.
(Iii) P1 Ab = P1 A P1 B.
(iv) pa a = p a.