Parenteral Dosage Form
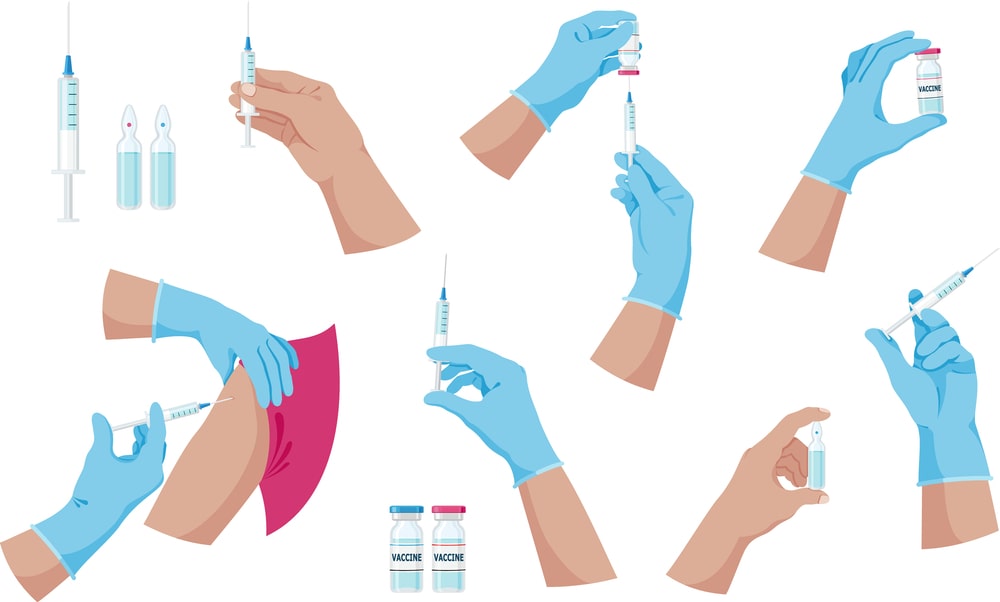
Parenteral Dosage Form - For patients taking penicillin g by mouth: Web a parenteral dosage is a sterile drug product, which is presented in the form of solution, suspension, emulsion, or reconstituted lyophilized powder, suitable for administration by injection. The iv route is the fastest method for delivering systemic drugs Eur.) commission adopted the revised version of the dosage form monograph on parenteral preparations (0520) which gives mandatory quality requirements for a large number of medicinal products on the european market. + bloodstream + muscle + skin + fatty layer just below the skin. Parenterals are sterile preparations that are injected intravascularly, administered into body tissues or into visceral cavities. Parenteral dosage forms are intended for administration as an injection or infusion. Typical routes of administration of a parenteral dosage form include subcutaneous, intramuscular, and intravenous delivery. Although usually aqueous, they may be mixtures of water with glycols, alcohol, or other nonaqueous solvents. This document is reference material for investigators and other fda personnel.
Examples of medications delivered parenterally include insulin, opioid analgesics, vaccines, and antibiotics, amongst other drugs. Web a parenteral dosage is a sterile drug product, which is presented in the form of solution, suspension, emulsion, or reconstituted lyophilized powder, suitable for administration by injection. To ensure sterility, parenterals are prepared using • aseptic techniques • special clothing (gowns, masks, hair net, gloves) • laminar flow hoods placed in special rooms. For patients taking penicillin g by mouth: Common injection types are intravenous (into a vein), subcutaneous (under the skin), and intramuscular (into muscle). The tablet form of this medicine may be taken on a full or empty stomach. Web forms of pharmaceutical dosage. Web the parenteral route of drug delivery includes four types: Web nikkigala terms in this set (29) parenteral any drug or fluid injected into the body, usually through a needle. Parenteral dosages can be injected into what parts of the human body?
Web at its 167th session in june 2020, the european pharmacopoeia (ph. The parenteral route is useful for rapid medication delivery and for supplementing. Web last updated on tue, 20 dec 2022 | drug absorption solutions most injectable products are solutions. Although usually aqueous, they may be mixtures of water with glycols, alcohol, or other nonaqueous solvents. Production of the first clinical trial materials for a new pharmaceutical dosage form is a significant milestone event in the development of a pharmaceutical product. The four types of parenteral administration include intradermal, subcutaneous, intramuscular. Children 6 to 12 years of age—2 mg three or four times a day as needed. Route of administration and dosage form are aspects of drug delivery. + bloodstream + muscle + skin + fatty layer just below the skin. Parenterals the term derived from greek word ‛para’ outside & ‛enterone’ intestine.
Parenteral Dosage Calculations YouTube
Common injection types are intravenous (into a vein), subcutaneous (under the skin), and intramuscular (into muscle). Typical routes of administration of a parenteral dosage form include subcutaneous, intramuscular, and intravenous delivery. Children 6 to 12 years of age—2 mg three or four times a day as needed. The tablet form of this medicine may be taken on a full or.
Parenteral Dosage Form Solution Parmacy
Typical routes of administration of a parenteral dosage form include subcutaneous, intramuscular, and intravenous delivery. Parenteral dosage form presented by, yogita rayate m.pharm first year dept.of pharmaceutics rajarambapu college of pharmacy,kasegaon 15/11/2017 1 ; To ensure sterility, parenteral are prepared using. Although usually aqueous, they may be mixtures of water with glycols, alcohol, or other nonaqueous solvents. Parenterals are sterile.
Classification of Dosage Form Solution Parmacy
Web dosage forms (also called unit doses) are pharmaceutical drug products in the form in which they are marketed for use, with a specific mixture of active ingredients and inactive components ( excipients ), in a particular configuration (such as a capsule shell, for example), and apportioned into a particular dose. Web a parenteral dosage is a sterile drug product,.
Parenteral Dosage Form Solution Parmacy
Web the parenteral route of drug delivery includes four types: Web parenteral dosage form: Web parenteral method involves bypassing the intestine to get the drug directly and quickly into the blood. Web parenteral medications are administered by (1) subcutaneous injection—beneath the skin, in fat; For patients taking penicillin g by mouth:
Parenteral dosage form parenteral preparation pharmaceutics
Web a parenteral dosage is a sterile drug product, which is presented in the form of solution, suspension, emulsion, or reconstituted lyophilized powder, suitable for administration by injection. Parenterals the term derived from greek word ‛para’ outside & ‛enterone’ intestine. To ensure sterility, parenterals are prepared using • aseptic techniques • special clothing (gowns, masks, hair net, gloves) • laminar.
Introduction Parenteral Dosage form YouTube
This document is reference material for investigators and other fda personnel. To ensure sterility, parenterals are prepared using • aseptic techniques • special clothing (gowns, masks, hair net, gloves) • laminar flow hoods placed in special rooms. Parenteral medications may also be given intravenously (iv)—within the vein. Amoxicillin amoxicillin/clavulanate ampicillin penicillin v ampicillin mr. Web parenteral method involves bypassing the.
Classification of Dosage Form Solution Pharmacy
Parenteral medications may also be given intravenously (iv)—within the vein. Parenterals are sterile preparations that are injected intravascularly, administered into body tissues or into visceral cavities. Advantages of the parenteral route: Web the liquid form of this medicine is best taken with a full glass (8 ounces) of water on an empty stomach (either 1 hour before or 2 hours.
parenteral dosage form
To ensure sterility, parenteral are prepared using. Web at its 167th session in june 2020, the european pharmacopoeia (ph. Web parenteral medications are administered by (1) subcutaneous injection—beneath the skin, in fat; Advantages of the parenteral route: Infusions typically are given by intravenous route.
Formulation of parentral pdf
Parenterals the term derived from greek word ‛para’ outside & ‛enterone’ intestine. Infusions typically are given by intravenous route. For patients taking penicillin g by mouth: Although usually aqueous, they may be mixtures of water with glycols, alcohol, or other nonaqueous solvents. The tablet form of this medicine may be taken on a full or empty stomach.
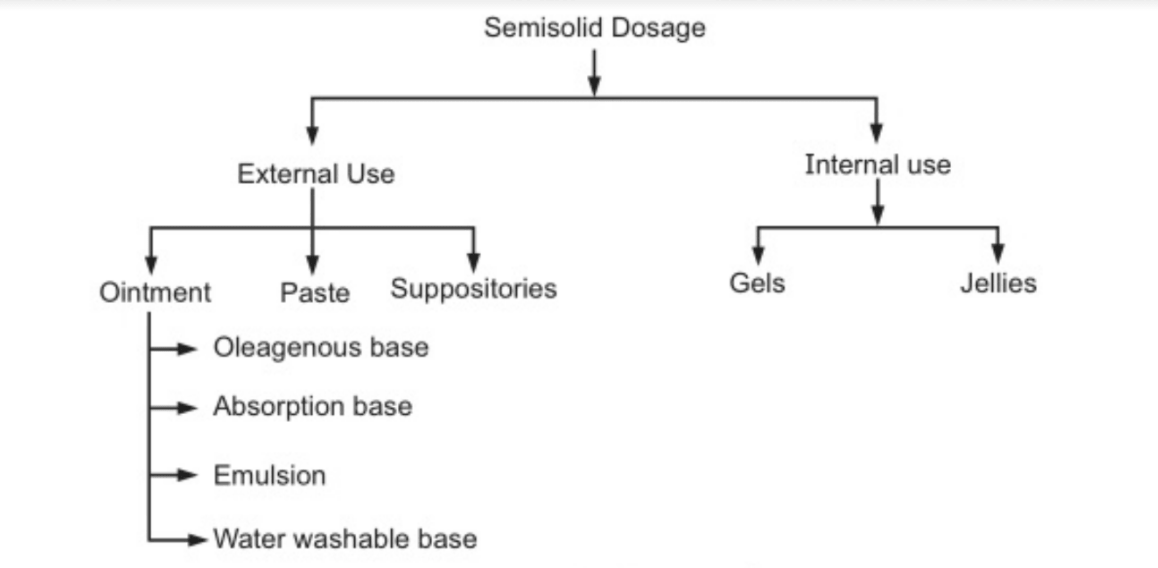
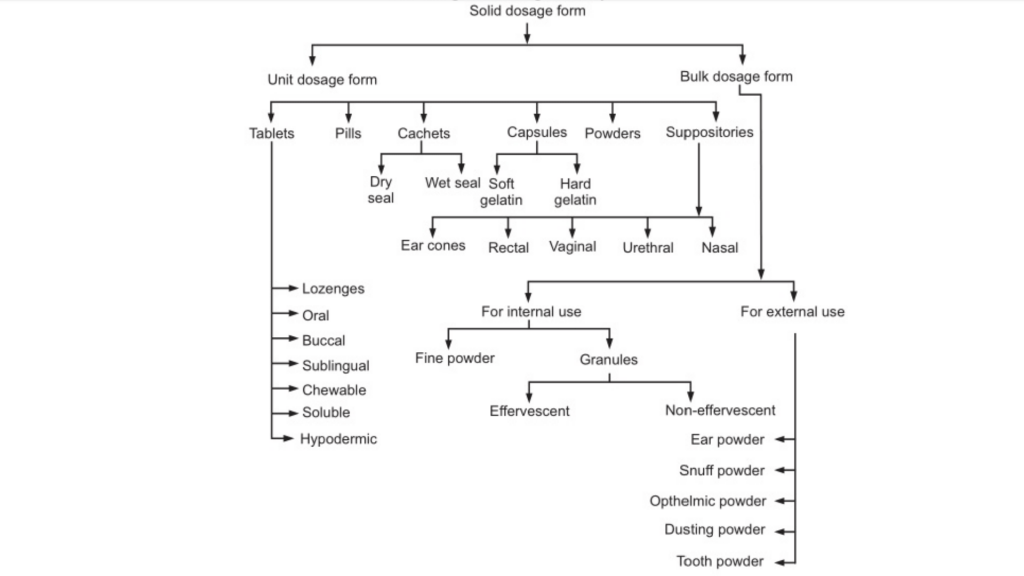
Types of Dosage Forms
+ bloodstream + muscle + skin + fatty layer just below the skin. Children 4 to 6 years of age—use and dose must be determined by your doctor. The four types of parenteral administration include intradermal, subcutaneous, intramuscular. (2) intramuscular (im) injection—within the muscle; Web at its 167th session in june 2020, the european pharmacopoeia (ph.
Parenteral Dosage Forms Are Intended For Administration As An Injection Or Infusion.
Parenteral medications may also be given intravenously (iv)—within the vein. Typical routes of administration of a parenteral dosage form include subcutaneous, intramuscular, and intravenous delivery. Examples of medications delivered parenterally include insulin, opioid analgesics, vaccines, and antibiotics, amongst other drugs. Web a parenteral dosage is a sterile drug product, which is presented in the form of solution, suspension, emulsion, or reconstituted lyophilized powder, suitable for administration by.
Web Nikkigala Terms In This Set (29) Parenteral Any Drug Or Fluid Injected Into The Body, Usually Through A Needle.
Parenterals are sterile preparations that are injected intravascularly, administered into body tissues or into visceral cavities. The four types of parenteral administration include intradermal, subcutaneous, intramuscular. Infusions typically are given by intravenous route. To ensure sterility, parenterals are prepared using • aseptic techniques • special clothing (gowns, masks, hair net, gloves) • laminar flow hoods placed in special rooms.
Route Of Administration And Dosage Form Are Aspects Of Drug Delivery.
Solutions of drugs suitable for parenteral administration are referred to as injections. + bloodstream + muscle + skin + fatty layer just below the skin. Web parenteral method involves bypassing the intestine to get the drug directly and quickly into the blood. Web dosage forms (also called unit doses) are pharmaceutical drug products in the form in which they are marketed for use, with a specific mixture of active ingredients and inactive components ( excipients ), in a particular configuration (such as a capsule shell, for example), and apportioned into a particular dose.
Production Of The First Clinical Trial Materials For A New Pharmaceutical Dosage Form Is A Significant Milestone Event In The Development Of A Pharmaceutical Product.
Routes of administration of parenteral products. To ensure sterility, parenteral are prepared using. Web parenteral dosage form: The iv route is the fastest method for delivering systemic drugs