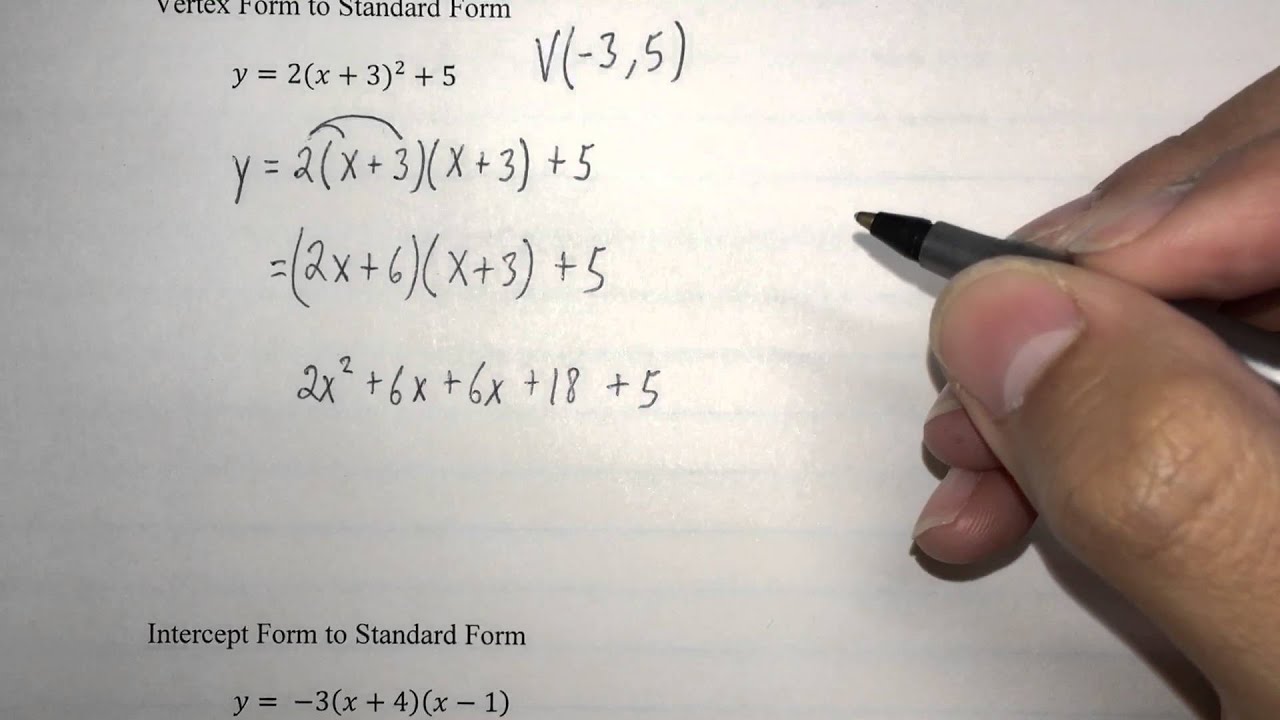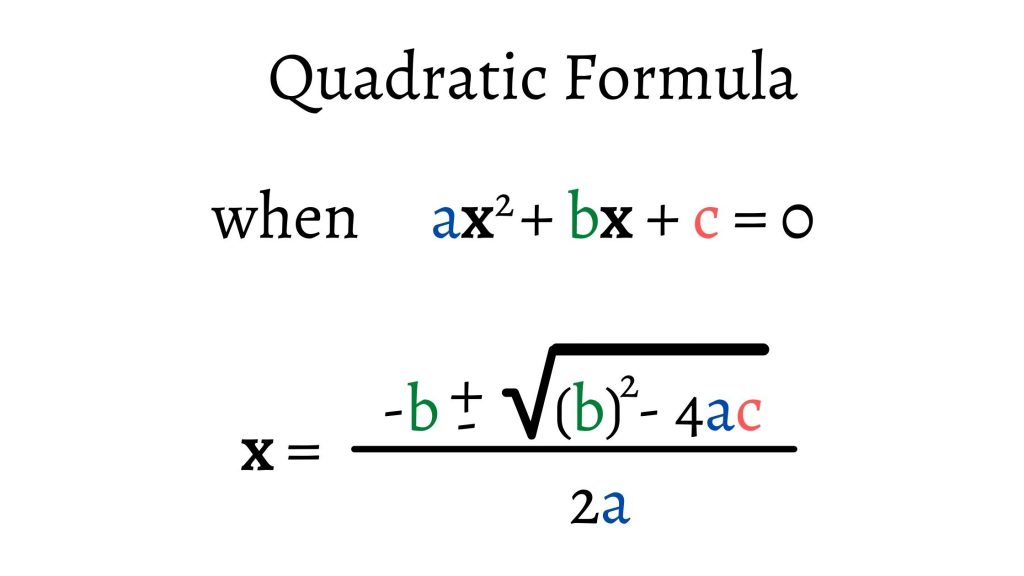How To Write A Quadratic Equation In Standard Form
How To Write A Quadratic Equation In Standard Form - 1) you can create a table of values: The graph of the quadratic function is in the form of a parabola. So long as a ≠ 0, you should be able to factor the quadratic equation. When the discriminant ( b2−4ac) is: Ax² + bx + c = 0 vertex form : Web three forms for representing quadratic equations. F (x) = ax² + bx + c = 0 Zero, there is one real solution. Web a {x}^ {2}+bx+c=0 ax2 + bx + c = 0. You will also know how to identify the values of a, b and c.
What is the quadratic formula? The standard form of a. Web learn how to write a quadratic equation in standard form by completing the square in this video by mario's math tutoring. You may also see the standard form called a general quadratic equation, or the general form. Web this video will demonstrate and show you the process on how to write quadratic equations in standard form. Positive, there are 2 real solutions. The graph of a quadratic function is a parabola. Then substitute in the values of a, b, c. Web quadratic functions can be represented in 3 forms: Web let α and β be the roots of quadratic equation in the general form:
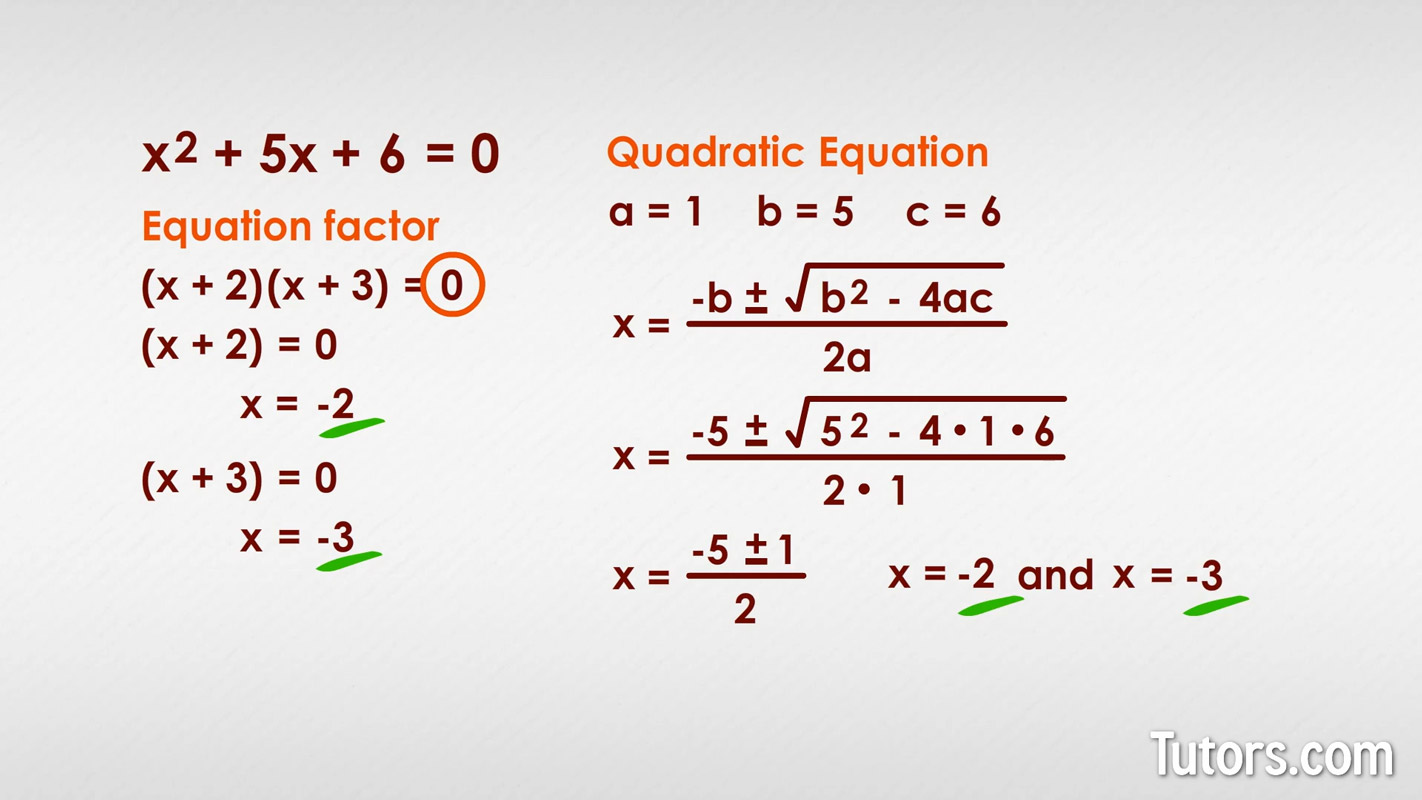
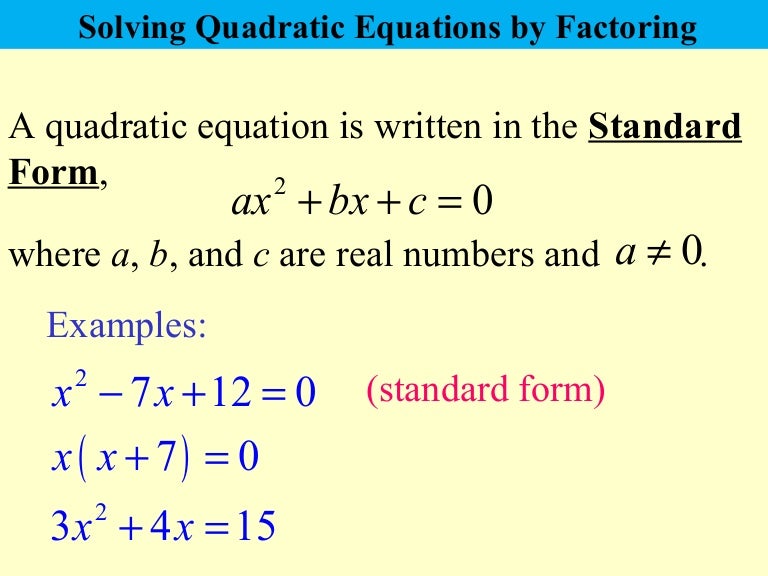
Web quadratic equation in standard form: Positive, there are 2 real solutions. Negative, there are 2 complex solutions. Web a quadratic equation in standard form is ax 2 + bx + c = 0. The graph of a quadratic function is a parabola. To solve a quadratic equation, use the quadratic formula: Web three forms for representing quadratic equations. Ax2 +bx+c = 0 a x 2 + b x + c = 0. The formulas for solving quadratic equations can be write as: X = −b ± √ (b2 − 4ac) 2a.
Standard Form Quadratic Equation Here's What People Are Saying About
Web the standard form of the quadratic function is f(x) = ax 2 +bx+c where a ≠ 0. Zero, there is one real solution. Ax2 +bx+c = 0 a x 2 + b x + c = 0. Quadratic equations can be factored. So long as a ≠ 0, you should be able to factor the quadratic equation.
Write Quadratic Equations in Standard Form YouTube
Ax2 + bx + c = 0. Web a quadratic equation in standard form is ax 2 + bx + c = 0. Web the standard form of the quadratic function is f(x) = ax 2 +bx+c where a ≠ 0. X = −b ± √ (b2 − 4ac) 2a. Sometimes, though, this gets confusing or messy, or you cannot.
Equation of a Quadratic Function in Standard Form YouTube
So long as a ≠ 0, you should be able to factor the quadratic equation. Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: This video contains plenty of example show more Ax2 +bx+c = 0 a x 2 + b x + c = 0. B^2 b2 can’t be negative, so if b b
The Quadratic Formula. Its Origin and Application IntoMath
Web write the quadratic equation in standard form 168,142 views jun 12, 2018 2.9k dislike share save escol emmanuel 30.8k subscribers how to write the quadratic equation. Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: The graph of a quadratic function is a parabola. 1) you can create a table of values: Quadratic equations can be factored.
Quadratic Formula InertiaLearning
Web according to my poorly written precalculus textbook, f(x)=(ax^2)+bx+c is not the standard form of a quadratic equation; Ax 2 + bx + c = 0. Web there are multiple ways that you can graph a quadratic. Zero, there is one real solution. So long as a ≠ 0, you should be able to factor the quadratic equation.
How To Write A Math Equation In Standard Form Tessshebaylo
B^2 b2 can’t be negative, so if b b The general form of a quadratic function is f(x) = ax2 + bx + c where a, b, and c are real numbers and a ≠ 0. Web the range of a quadratic function written in standard form f (x) = a (x − h) 2 + k f (x) =.
Standard Form of Quadratic Equation with Examples
B^2 b2 can’t be negative, so if b b Quadratic equations can be factored. Web this algebra video tutorial explains how to write the quadratic equation in standard form given 2 solutions or 3 points. Web to solve a quadratic equation using the quadratic formula. Web what is the standard form of a quadratic?
Writing a quadratic function in standard form (college algebra) YouTube
To solve a quadratic equation, use the quadratic formula: The standard form of a. Quadratic equations can be factored. Using the discriminant, \(b^2−4ac\), to determine the number of solutions of a quadratic equation The general form of a quadratic function is f(x) = ax2 + bx + c where a, b, and c are real numbers and a ≠ 0.
Quadratic equations that factorise
Web quadratic functions can be represented in 3 forms: What is the quadratic formula? Ax2 +bx+c = 0 a x 2 + b x + c = 0. Web tips when using the quadratic formula be careful that the equation is arranged in the right form: 1) you can create a table of values:
How To Write A Quadratic Equation In Standard Form
You will also know how to identify the values of a, b and c. Quadratic equations can be factored. Using the discriminant, \(b^2−4ac\), to determine the number of solutions of a quadratic equation Pick a value of x and calculate y to get points and graph the parabola. 1) you can create a table of values:
Web To Solve A Quadratic Equation Using The Quadratic Formula.
The range of a quadratic function written in standard form with a negative a a value is f (x) ≤ k. You may also see the standard form called a general quadratic equation, or the general form. Identify the a, b, c values. Ax² + bx + c = 0 vertex form :
Ax2 + Bx + C = 0.
Negative, there are 2 complex solutions. You will also know how to identify the values of a, b and c. What is the quadratic formula? Standard form of quadratic equation:
Web A Quadratic Equation In Standard Form Is Ax 2 + Bx + C = 0.
Quadratic equations can be factored. Zero, there is one real solution. Ax2 +bx+c = 0 a x 2 + b x + c = 0. Web the standard form of the quadratic function is f(x) = ax 2 +bx+c where a ≠ 0.
The Discriminant Of A Quadratic Equation Ax 2 + Bx + C = 0 Is Given By.
Sometimes, though, this gets confusing or messy, or you cannot factor it. 2) if the quadratic is factorable, you can use the techniques shown in this video. Ax^2 + bx + c = 0 ax2 + bx + c = 0 or it won’t work! The general form of a quadratic function is f(x) = ax2 + bx + c where a, b, and c are real numbers and a ≠ 0.