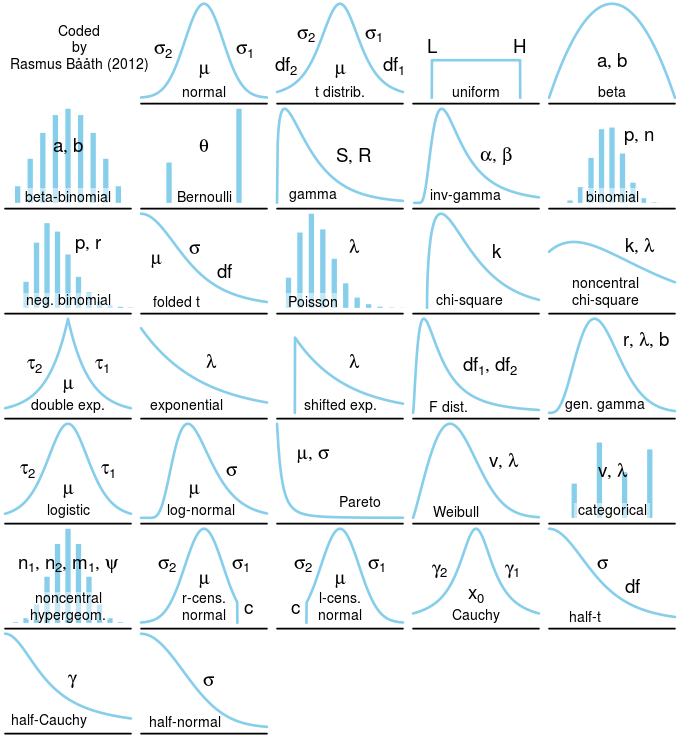
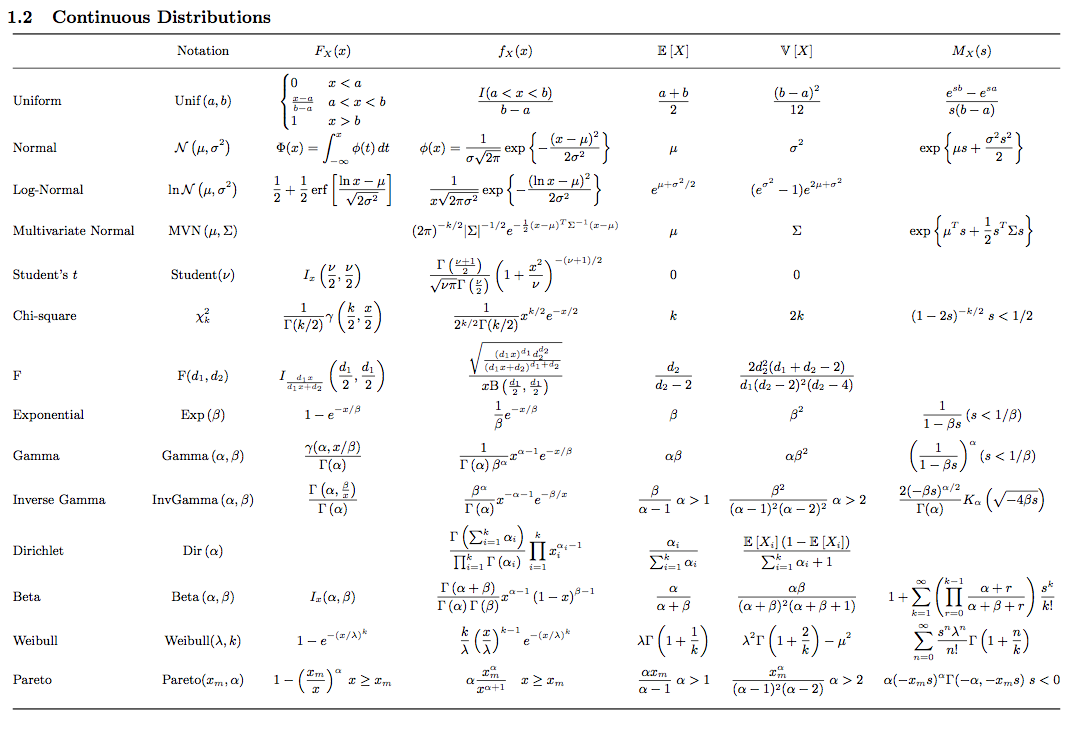
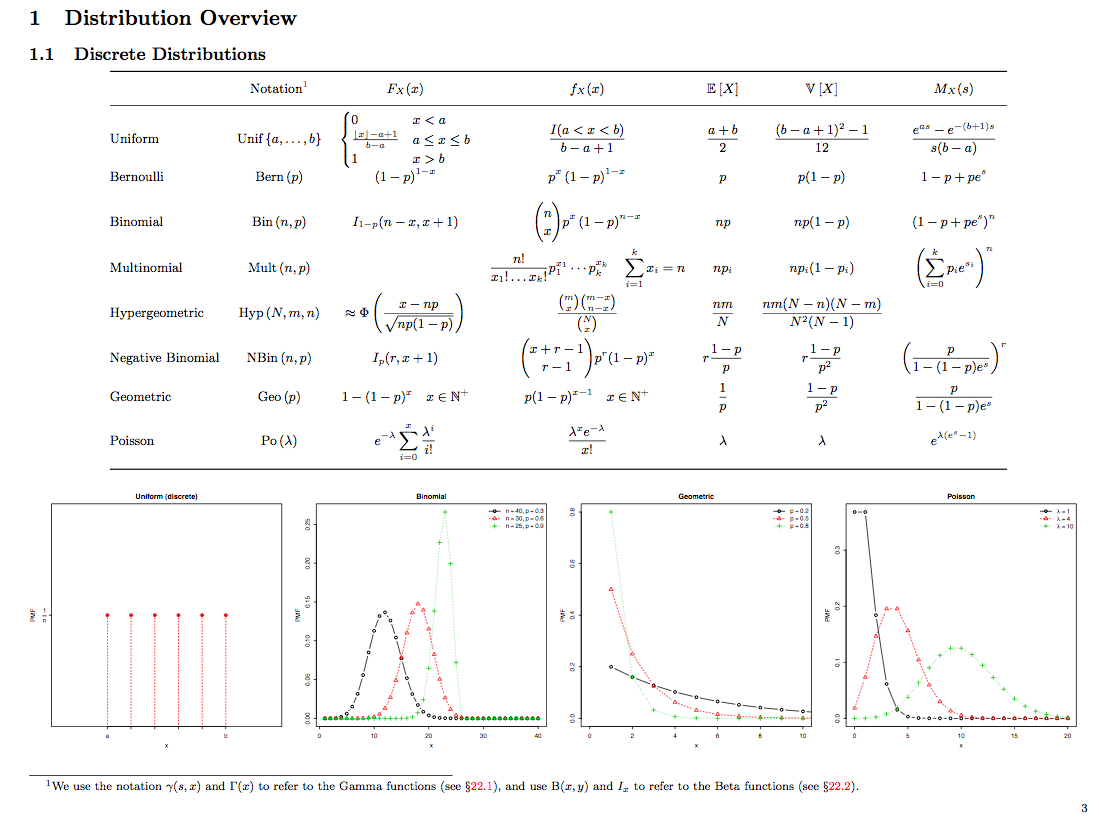
Distributions Cheat Sheet
Distributions Cheat Sheet - 2 probability the chance of a certain event. [ ( )] standard deviation of a probability distribution: B means a is less than b. Web a (v) a < b p 1. A b means that a is less than or the same as b. Web probability distributions have parameters that control the exact shape of the distribution. { the point that cuts the interval (a+b) [a; Material based on joe blitzstein's. Web sheets interchange “r” and “x” for number of successes chapter 5 discrete probability distributions: Web common probability distributions nathaniel e.
For example, the binomial probability distribution describes a random variable that represents the number of. Web a (v) a < b p 1. A b means that a is less than or the same as b. Web sheets interchange “r” and “x” for number of successes chapter 5 discrete probability distributions: [ ( )] standard deviation of a probability distribution: B means a is less than b. A > b means a is bigger than b. 22 mean of a discrete probability distribution: Helwig university of minnesota 1 overview as a reminder, a random variable x has an associated probability distribution f ( ), also know as a cumulative distribution function. { the point that cuts the interval (a+b) [a;
Helwig university of minnesota 1 overview as a reminder, a random variable x has an associated probability distribution f ( ), also know as a cumulative distribution function. A > b means a is bigger than b. Material based on joe blitzstein's. A b means that a is less than or the same as b. Web common probability distributions nathaniel e. [ ( )] standard deviation of a probability distribution: 2 probability the chance of a certain event. Web probability distributions have parameters that control the exact shape of the distribution. { the point that cuts the interval (a+b) [a; Web a (v) a < b p 1.
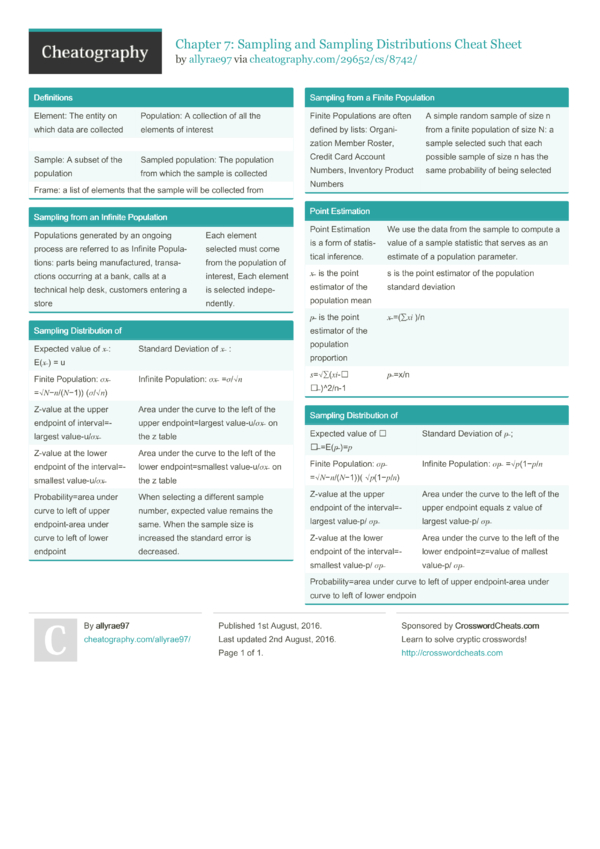
Chapter 7 Sampling and Sampling Distributions Cheat Sheet by allyrae97
B means a is less than b. For example, the binomial probability distribution describes a random variable that represents the number of. A > b means a is bigger than b. A b means that a is less than or the same as b. [ ( )] standard deviation of a probability distribution:
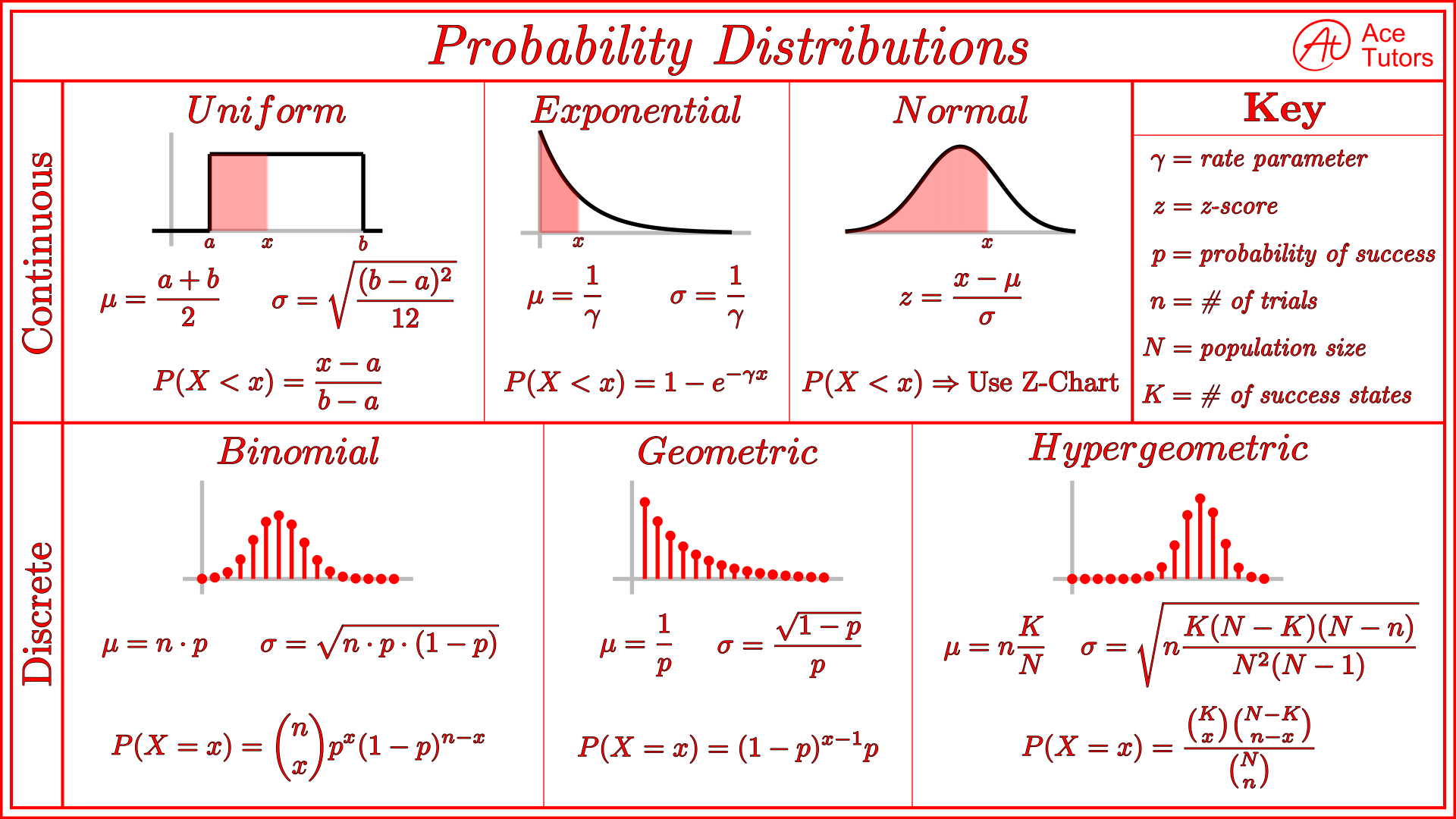
Probability Distribution Cheat Sheet Calculus Ace Tutors Blog
Material based on joe blitzstein's. Web common probability distributions nathaniel e. B means a is less than b. A b means that a is less than or the same as b. For example, the binomial probability distribution describes a random variable that represents the number of.
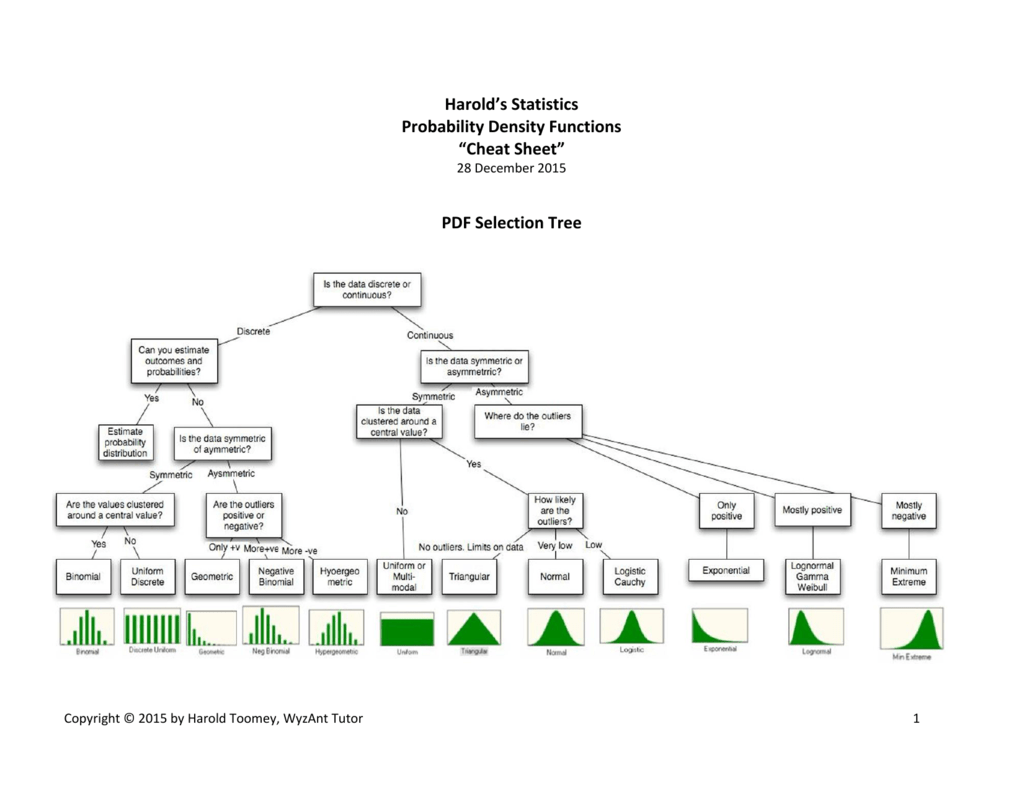
Harold's Statistics PDFs Cheat Sheet
[ ( )] standard deviation of a probability distribution: Material based on joe blitzstein's. A b means that a is less than or the same as b. Web a (v) a < b p 1. For example, the binomial probability distribution describes a random variable that represents the number of.
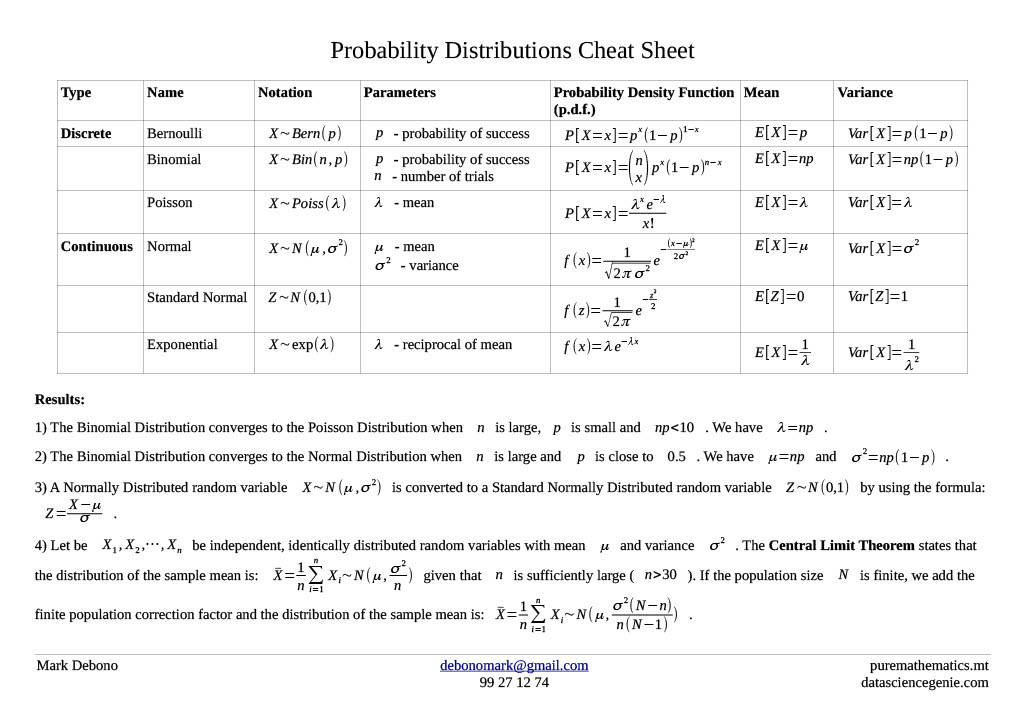
Probability Distribution Cheat Sheet puremathematics.mt
[ ( )] standard deviation of a probability distribution: 22 mean of a discrete probability distribution: { the point that cuts the interval (a+b) [a; A b means that a is less than or the same as b. B means a is less than b.
SOLUTION Probability distributions cheat sheet for data science
2 probability the chance of a certain event. A > b means a is bigger than b. Helwig university of minnesota 1 overview as a reminder, a random variable x has an associated probability distribution f ( ), also know as a cumulative distribution function. [ ( )] standard deviation of a probability distribution: 22 mean of a discrete probability.
the table shows different types of numbers and their corresponding
B means a is less than b. Web probability distributions have parameters that control the exact shape of the distribution. 22 mean of a discrete probability distribution: A > b means a is bigger than b. Web sheets interchange “r” and “x” for number of successes chapter 5 discrete probability distributions:
Common Probability Distributions Cheat Sheet Data Science and Machine
22 mean of a discrete probability distribution: A b means that a is less than or the same as b. A > b means a is bigger than b. For example, the binomial probability distribution describes a random variable that represents the number of. Web sheets interchange “r” and “x” for number of successes chapter 5 discrete probability distributions:
Matthias Vallentin Probability and Statistics Cheat Sheet
B means a is less than b. 22 mean of a discrete probability distribution: A > b means a is bigger than b. Helwig university of minnesota 1 overview as a reminder, a random variable x has an associated probability distribution f ( ), also know as a cumulative distribution function. Web a (v) a < b p 1.
math notation cheat sheet Web cheatsheet bashooka es6
Web probability distributions have parameters that control the exact shape of the distribution. A b means that a is less than or the same as b. Web sheets interchange “r” and “x” for number of successes chapter 5 discrete probability distributions: A > b means a is bigger than b. For example, the binomial probability distribution describes a random variable.
GitHub wzchen/probability_cheatsheet A comprehensive 10page
A > b means a is bigger than b. Web probability distributions have parameters that control the exact shape of the distribution. 2 probability the chance of a certain event. A b means that a is less than or the same as b. For example, the binomial probability distribution describes a random variable that represents the number of.
2 Probability The Chance Of A Certain Event.
A > b means a is bigger than b. [ ( )] standard deviation of a probability distribution: Material based on joe blitzstein's. B means a is less than b.
22 Mean Of A Discrete Probability Distribution:
A b means that a is less than or the same as b. Web common probability distributions nathaniel e. For example, the binomial probability distribution describes a random variable that represents the number of. { the point that cuts the interval (a+b) [a;
Web Probability Distributions Have Parameters That Control The Exact Shape Of The Distribution.
Web a (v) a < b p 1. Web sheets interchange “r” and “x” for number of successes chapter 5 discrete probability distributions: Helwig university of minnesota 1 overview as a reminder, a random variable x has an associated probability distribution f ( ), also know as a cumulative distribution function.